The Design of the Simplest Self-Replicating living cell
One of the most common arguments by atheists, when explaining that biological cells are complex factories, is, that cells are Self-replicating, while human-made factories are not. This is, however, a self-defeating argument, because it is not taken into consideration, that self-replication is the epitome of manufacturing advance and achievement, far from being realized by man-made factories.
Self-replication had to emerge and be implemented first, which rises the unbridgeable problem that DNA replication is irreducibly complex :
Evolution is not a capable driving force to make the DNA replicating complex, because evolution depends on cell replication through the very own mechanism we try to explain. It takes proteins to make DNA replication happen. But it takes the DNA replication process to make proteins. That’s a catch 22 situation.
In fact, the highest degree of manufacturing performance, excellence, precision, energy efficiency, adaptability to external change, economy, refinement and intelligence of production automatization ( at a scale from 1 -100, = 100 ) we find in proceedings adopted by each cell, analogous to a factory, and biosynthesis pathways and processes in biology. A cell uses a complex web of metabolic pathways, each composed of chains of chemical reactions in which the product of one enzyme becomes the substrate of the next. In this maze of pathways, there are many branch points where different enzymes compete for the same substrate. The system is so complex that elaborate controls are required to regulate when and how rapidly each reaction occurs. Like a factory production line, each enzyme catalyzes a specific reaction, using the product of the upstream enzyme, and passing the result to the downstream enzyme.
ORIGINS AND EVOLUTION OF LIFE An Astrobiological Perspective MURIEL GARGAUD, page 58
Self-replication is the ability of a system to produce a copy of itself on its own; it is one of the essential characteristics which has most intrigued and impassioned disciples of artificial life. Biology, and in particular the faculty of self-replication, fascinated von Neumann to the extent that he devoted the majority of his final years in science to it. The comparison of a cell to a computer and of a genome to a code requires an understanding of how the computer itself is able to be created out of this code. Let us follow, step by step, the reasoning of von Neumann, as it is the perfect illustration of an ‘artificial life’ type of approach with no material instantiation but just pure functions or rules. To a the sequence of purely functional questions and showing an almost complete ignorance of biological materiality, his reasoning led to a logical explanation, the content of which retraces astonishingly closely those lessons we have since learned about the way biology functions. Von Neumann works on the principle that a universal constructor C must exist, which is based on the plan that some kind of machine P M (P the plan, M the machine) must be capable of constructing the machine M P . The question of self-replication which is then raised is ‘Is this universal constructor capable of constructing itself?’ In order to do so, it must, following the example of other construction products, have a plan of what it wants to construct; in this specific case, it is the constructor’s plan P C .
Any OOL credible explanation should provide answers to the following questions:
How the self-describing information (of so many varieties) residing in the cell originated?
How the energy generation and transport function originated?
How the material identification function and the material extraction function originated?
How the fabrication function originated
How the transport and manipulation functions originated?
How the coordinated control of various functions originated?
How the whole sophisticated design of the cell originated?
Is it reasonable to believe/accept that the cell resulted through random/natural processes when the 21st century scientists are only beginning to understand only SOME OF THE INTERNALS of a cell?
Is it reasonable to believe/accept that the cell resulted through random/natural processes when the 21st century scientists and engineers are still not able to design and create an artificial cell?
It seems to me, that a pre-existing intelligence to project self-replication is essential. Soft-and hardware is interdependent, as Davies puts it.
Paul Davies: the fifth miracle page 62
Due to the organizational structure of systems capable of processing algorithmic (instructional) information, it is not at all clear that a monomolecular system – where a single polymer plays the role of catalyst and informational carrier – is even logically consistent with the organization of information flow in living systems, because there is no possibility of separating information storage from information processing (that being such a distinctive feature of modern life). As such, digital-first systems (as currently posed) represent a rather trivial form of information processing that fails to capture the logical structure of life as we know it. 1
We need to explain the origin of both the hardware and software aspects of life, or the job is only half-finished. Explaining the chemical substrate of life and claiming it as a solution to life’s origin is like pointing to silicon and copper as an explanation for the goings-on inside a computer. It is this transition where one should expect to see a chemical system literally take-on “a life of its own”, characterized by informational dynamics which become decoupled from the dictates of local chemistry alone (while of course remaining fully consistent with those dictates). Thus the famed chicken-or-egg problem (a solely hardware issue) is not the true sticking point. Rather, the puzzle lies with something fundamentally different, a problem of causal organization having to do with the separation of informational and mechanical aspects into parallel causal narratives. The real challenge of life’s origin is thus to explain how instructional information control systems emerge naturally and spontaneously from mere molecular dynamics.
https://reasonandscience.catsboard.com/t2221-the-hardware-and-software-of-the-cell-evidence-of-design
Von Neumann universal constructor
John von Neumann's Universal Constructor is a self-replicating machine in a cellular automata (CA) environment. It was designed in the 1940s, without the use of a computer. The fundamental details of the machine were published in von Neumann's book Theory of Self-Reproducing Automata, completed in 1966 by Arthur W. Burks after von Neumann's death.Von Neumann's goal was to specify an abstract machine which, when run, would replicate itself. In his design, the machine consists of three parts: a 'blueprint' for itself, a mechanism that can read any blueprint and construct the machine (sans blueprint) specified by that blueprint, and a 'copy machine' that can make copies of any blueprint. After the mechanism has been used to construct the machine specified by the blueprint, the copy machine is used to create a copy of that blueprint, and this copy is placed into the new machine, resulting in a faithful replication of the original machine.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Von_Neumann_universal_constructor
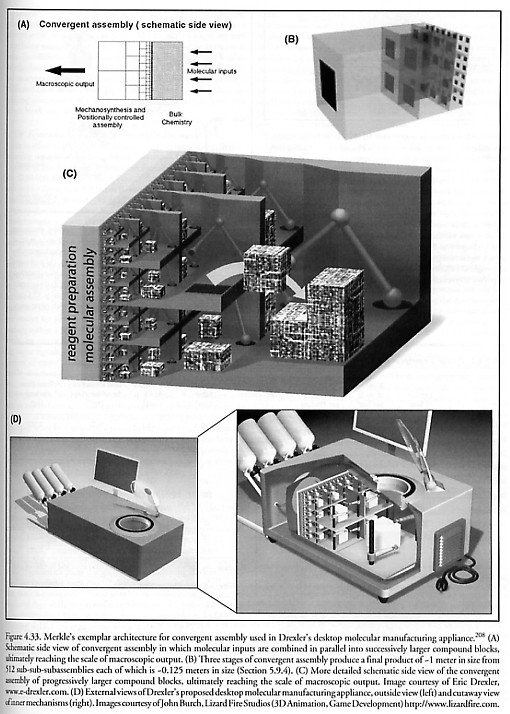
Drexler Nanofactory Replication System (1991-1992)
Following article shows the minimal structure of a cell that is required for self-replication to occur. It takes a lot of faith to believe, the cell could arise due to random natural chemical reactions.
Goals, Assumptions and Requirements
Goals:
Develop insights into internal design of the cell
Evaluate complexity in creating an artificial cell
Assumptions:
There is an intake of materials from the outside of cell
There is an output of waste materials from inside to outside of the cell
We assume throughout that we design for building an artificial cell – that need not have a biological basis (not built with carbon-based chemistry) but is rather a ‘clunky’ one (made from metal, plastic, semiconductors, etc.)
Requirements
The cell has an Enclosure to separate it and protect it from its environment
The cell is capable to create an identical copy of itself
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dCqb_hyFHEA
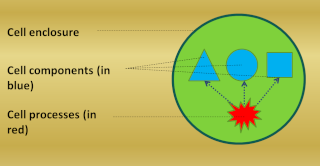
The Simplest Self-Replicator ( Cell ) Schematic Illustration
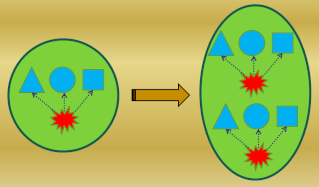
What happens during cell replication? – the “cloning” phase
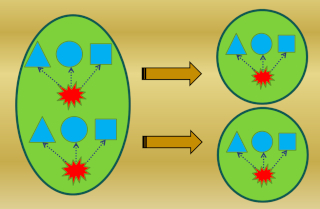
What happens during cell replication? – the “division” phase
What would have to happen during the replication of our artifical cell ?
Input materials processed through material extraction into good materials for fabrication of parts or for energy generation
Energy is generated and made available throughout the cell
Fabrication function starts to fabricate parts, components and assemblies for:
Cloning (creating copies) of all cell internal elements
Creating scaffolding elements for the growing cell interior
Creating new elements that are added to the growing enclosure
When the cloning of all original cell internal parts completed, the cell division starts:
The original cell content is now at (for example) “north pole” of the cell enclosure
The cloned cell content (the “nascent daughter cell”) is now at the “south pole” of the cell enclosure
The SSR enclosure and its content now divides at the “equatorial” plane and the separate “mother” (at North) and daughter (at South) cell emerge.
Now lets say someone would decide to try to make a artifical cell, how would it be able to clone accurately all its internal parts?
It would not be possible by using a mechanical copy process – similar with that used to duplicate house keys. Using internal design information would be required in combination with computer controlled roboters.
Control of Input Flow, Functions of Material Identification and Material Extraction
Input Flow Control function
Opens/closes the enclosure input gateways
Acts based on the nature of input material/part and commands from other functions
Material and Parts Identification function
Identifies nature of input materials and parts
Tags input materials and parts, manufactured materials and fabricated parts with type Id (bar code like)
Material Extraction function
Uses specific processes to extract manufacturing materials from raw materials
Uses specific machinery and parts
Input Flow Control Function
Our cell needs to have gates which permit material to get in or out. Further it needs to be able to recognize and identify what the incoming materials in are made of. So the cell must be able to act like a roboter, programmed and automatically, by itself, to recognize the materials and permit or refuse their entrance.
Function of Energy Generation and internal transport highways and transport vessels
The cell needs to be able to generate energy from raw or processed materials. It needs to be able to transport and distribute materials, and managing energy requirements
( electricity ) It has to use special machinery: generators, transformers, converters.
An open question is, what material basis to provide energy: fuel, oil, coal, chemical, atomic etc.
Transport function:
Transport materials and parts/components
Uses containers, conduits, wires, carriers
Transports also energy and information
Ability of chain supply, recycling and function of output Flow control
Supply Chain function:
Ensures steady supply of materials, energy and parts
Coordinating and scheduling capability
Recycling function:
Re-introduce useful materials and parts in the fabrication cycle
Selects materials and parts as refuse; cleans spaces
Output Flow Control function:
Sends refuse materials and parts outside the cell
Controls output gateways of the enclosure
Storage of a catalog of all materials , Construction Plan , registration of construction status
Bill of Materials function:
Catalogs of all materials and all parts
For each element: its composition in sub-elements and materials
Construction Plan function:
Catalog of construction plan and design of all parts, components, assemblies including the cell as a whole
Catalog of all processes
Catalog of all procedures
Construction Status function:
Uses replicas of construction plans to mark construction progress
Status updated by functions involved in fabrication and construction
Hability of Manipulation , Fabrication of all parts, and Fabrication quality Control
Manipulation function:
Ability to “grab”, “handle”, “manipulate” materials, parts, components
Implemented with robot arm – like machinery
Fabrication Function:
Must be able to fabricate any and all cell parts and components
In particular able to fabricate all cell machinery
Fabrication Control function:
Follows the construction plans
Commands the fabrication function to manufacture next elements in the plan
Function of Communication and Notification, Growth Function through scaffolding and Enclosure Growth
Communication and Notification function:
Facilitates communication between the “control” centers and “execution” centers
Notifications from “executor” to “controller”
Scaffolding Growth function:
Controls construction and growth of cell scaffolding
Mostly on the “daughter” cell side
Enclosure Growth function:
Controls the construction and growth of the enclosure
Addition of enclosure gateways; flexible geometry
Cloning Function, Hability of cell Division and Replication
Cloning function
Choreographs the cloning phase
Coordinates fabrication of the clone and growth of scaffolding and enclosure
Copies info catalogs and software into the cloned parts
Division function:
Choreograph the cell division phase
“start the engines” of the “daughter” cell just before division completes
Replication function:
Highest level function:
Implements the designer commandments:
- Grow and
- Multiply
What we learned about the artificial Cell?
The cell must be designed for growth and division: the enclosure must support changing surface, volume and shape
The cell must contain detailed, structured, cohesive descriptive information that must be accurately and integrally passed to next cell generation.
Required information:
-all used materials: identification, description, characteristics
-manufacturing materials: extraction procedures and processes
-bill of materials for all fabricated parts, components and assemblies
-procedures and processes for energy generation, storage (if needed) transportation and management
-construction plans for all fabricated parts, components and assemblies including the cell itself.
-all fabrication processes and procedures
-all assemblage procedures
-all recycling procedures and processes
The cell
must contain advanced materials and parts identification capabilities as well as material extraction capabilities
must contain sophisticated, fully automated and computer-controlled capabilities for energy generation, transportation, management and distribution
must contain very sophisticated fabrication and assemblage capabilities that must be information-driven for full automation and computer control.
must posses advanced computing (information processing) capabilities as well as good information communication capabilities.
must control its many parts and layered functions through very advanced software running on cell-computer(-like) machinery.
Above all: the cell must be based on a very sophisticated design that harmoniously, precisely and completely provides full automation and self-sufficiency for all machinery and processes that happens inside an cell during its growth, division and replication.
The design of a cell can be successful only if it is harmoniously integrated and precisely coordinated with the design and characteristics of its environment.
An artificial cell most probable must contain:
a material mining sub-unit
a metallurgic subunit
a chemical plant
a power plant
an electricity distribution network
a network of avenues, alleys and conduits for robotized transportation
a semiconductor manufacturing plant
a computer manufacturing plant
an extended communication network connecting by wire or rather wirelessly all plants and robots
a software manufacturing plant and software distribution and installation agents.
a materials and parts recycling and refuse management plant
an army of intelligent robots for transportation and manipulation
a highly sophisticated distributed, multi-layered software system that controls in a cohesive manner all plants, robots and communications.
Robots made of classical components can make identical copies of themselves, but quantum machines can't.
Evaluating the Complexity of an artificial cell
The Cell: autonomous, computerized and automated
There is no comparable human engineering artifact in terms of:
Autonomy (materials, energy, fabrication closure, information closure, ‘intelligence’)
full manufacturing automation
spectrum of processes and fabrication types
No successful attempt so far on building a real autonomous artificial cell from scratch
Attempts so far:
software simulations
cellular automata
self-replicating software entities
RepRap – self replicating 3D printers
self-assembling Lego robots
Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS)
Craig Venter’s synthetic bacterial cell
Comparing a genuine artificial Cell with:
An advanced car manufacturing/assembly line:
many/most parts are fabricated elsewhere
not fully automated; many manual operations performed by humans
no material identification, material extraction capabilities
not so many process technologies involved
mostly an assembly operation
The Large Hadron Collider (HDC) in Switzerland
no fabrication
not comparable in terms of automation, process diversity
The Martian Rover
some good amount of autonomy
no fabrication
The Metaphysics of It All
A reasonable scientific hypothesis is that the Master Designer designed wisely all life types for this successful cohabitation of Homo Sapiens
with all other types of life.
More so it is hypothesized (again scientifically) that the Earth, the Solar System, the Milky Way Galaxy and the Whole Universe was designed and finely adjusted by the Master Designer so that Homo Sapiens and all other life forms have a comfortable and enjoyable place to live.
More so, besides having a comfortable place to live Homo Sapiens have plenty of cell types to study and to marvel at the fabulous skills of the Master Designer revealed so blatantly in His cell designs.
More so, besides having amazing engineering feats to discover and admire, the Homo Sapiens has a rightful Master Designer to praise and worship all his life.
A number of researchers have concluded that the spontaneous origin of life cannot be explained by known laws of physics and chemistry. Many seek “new” laws which can account for life’s origin. Why are so many unwilling to simply accept what the evidence points to: that the theory of evolution itself is fundamentally implausible? Dean Kenyon answers, “Perhaps these scientists fear that acceptance of this conclusion would leave open the possibility (or the necessity) of a supernatural origin of life” (p.viii).
1
If an atheist dismisses it out hand, it is either because he has not thought seriously about the huge task and difficulty required to make a first living self-replicating cell and why natural mechanisms are inadequate. Or he is committed to his naturalistic worldview in a way, that he is unwilling or incapable of recognizing the flaws of his worldview and convictions. In that case, only a miracle to change his mind. But a conversion is always a miracle, anyway..... Infront of the powerful facts and extraordinary requirements to make a self-replicating machine exposed, any argument brought forward by atheists is like dim and helpless excuses in order to reject an intelligent designer. Not based on scientific eloquent arguments, but wishful and obscured thinking, and bad will.
1) http://www.cogmessenger.org/wp-content/uploads/2013/06/Mystery_of_Life_Origin.pdf
2. ORIGINS AND EVOLUTION OF LIFE An Astrobiological Perspective MURIEL GARGAUD, page 58
One of the most common arguments by atheists, when explaining that biological cells are complex factories, is, that cells are Self-replicating, while human-made factories are not. This is, however, a self-defeating argument, because it is not taken into consideration, that self-replication is the epitome of manufacturing advance and achievement, far from being realized by man-made factories.
Self-replication had to emerge and be implemented first, which rises the unbridgeable problem that DNA replication is irreducibly complex :
Evolution is not a capable driving force to make the DNA replicating complex, because evolution depends on cell replication through the very own mechanism we try to explain. It takes proteins to make DNA replication happen. But it takes the DNA replication process to make proteins. That’s a catch 22 situation.
In fact, the highest degree of manufacturing performance, excellence, precision, energy efficiency, adaptability to external change, economy, refinement and intelligence of production automatization ( at a scale from 1 -100, = 100 ) we find in proceedings adopted by each cell, analogous to a factory, and biosynthesis pathways and processes in biology. A cell uses a complex web of metabolic pathways, each composed of chains of chemical reactions in which the product of one enzyme becomes the substrate of the next. In this maze of pathways, there are many branch points where different enzymes compete for the same substrate. The system is so complex that elaborate controls are required to regulate when and how rapidly each reaction occurs. Like a factory production line, each enzyme catalyzes a specific reaction, using the product of the upstream enzyme, and passing the result to the downstream enzyme.
ORIGINS AND EVOLUTION OF LIFE An Astrobiological Perspective MURIEL GARGAUD, page 58
Self-replication is the ability of a system to produce a copy of itself on its own; it is one of the essential characteristics which has most intrigued and impassioned disciples of artificial life. Biology, and in particular the faculty of self-replication, fascinated von Neumann to the extent that he devoted the majority of his final years in science to it. The comparison of a cell to a computer and of a genome to a code requires an understanding of how the computer itself is able to be created out of this code. Let us follow, step by step, the reasoning of von Neumann, as it is the perfect illustration of an ‘artificial life’ type of approach with no material instantiation but just pure functions or rules. To a the sequence of purely functional questions and showing an almost complete ignorance of biological materiality, his reasoning led to a logical explanation, the content of which retraces astonishingly closely those lessons we have since learned about the way biology functions. Von Neumann works on the principle that a universal constructor C must exist, which is based on the plan that some kind of machine P M (P the plan, M the machine) must be capable of constructing the machine M P . The question of self-replication which is then raised is ‘Is this universal constructor capable of constructing itself?’ In order to do so, it must, following the example of other construction products, have a plan of what it wants to construct; in this specific case, it is the constructor’s plan P C .
Any OOL credible explanation should provide answers to the following questions:
How the self-describing information (of so many varieties) residing in the cell originated?
How the energy generation and transport function originated?
How the material identification function and the material extraction function originated?
How the fabrication function originated
How the transport and manipulation functions originated?
How the coordinated control of various functions originated?
How the whole sophisticated design of the cell originated?
Is it reasonable to believe/accept that the cell resulted through random/natural processes when the 21st century scientists are only beginning to understand only SOME OF THE INTERNALS of a cell?
Is it reasonable to believe/accept that the cell resulted through random/natural processes when the 21st century scientists and engineers are still not able to design and create an artificial cell?
It seems to me, that a pre-existing intelligence to project self-replication is essential. Soft-and hardware is interdependent, as Davies puts it.
Paul Davies: the fifth miracle page 62
Due to the organizational structure of systems capable of processing algorithmic (instructional) information, it is not at all clear that a monomolecular system – where a single polymer plays the role of catalyst and informational carrier – is even logically consistent with the organization of information flow in living systems, because there is no possibility of separating information storage from information processing (that being such a distinctive feature of modern life). As such, digital-first systems (as currently posed) represent a rather trivial form of information processing that fails to capture the logical structure of life as we know it. 1
We need to explain the origin of both the hardware and software aspects of life, or the job is only half-finished. Explaining the chemical substrate of life and claiming it as a solution to life’s origin is like pointing to silicon and copper as an explanation for the goings-on inside a computer. It is this transition where one should expect to see a chemical system literally take-on “a life of its own”, characterized by informational dynamics which become decoupled from the dictates of local chemistry alone (while of course remaining fully consistent with those dictates). Thus the famed chicken-or-egg problem (a solely hardware issue) is not the true sticking point. Rather, the puzzle lies with something fundamentally different, a problem of causal organization having to do with the separation of informational and mechanical aspects into parallel causal narratives. The real challenge of life’s origin is thus to explain how instructional information control systems emerge naturally and spontaneously from mere molecular dynamics.
https://reasonandscience.catsboard.com/t2221-the-hardware-and-software-of-the-cell-evidence-of-design
Von Neumann universal constructor
John von Neumann's Universal Constructor is a self-replicating machine in a cellular automata (CA) environment. It was designed in the 1940s, without the use of a computer. The fundamental details of the machine were published in von Neumann's book Theory of Self-Reproducing Automata, completed in 1966 by Arthur W. Burks after von Neumann's death.Von Neumann's goal was to specify an abstract machine which, when run, would replicate itself. In his design, the machine consists of three parts: a 'blueprint' for itself, a mechanism that can read any blueprint and construct the machine (sans blueprint) specified by that blueprint, and a 'copy machine' that can make copies of any blueprint. After the mechanism has been used to construct the machine specified by the blueprint, the copy machine is used to create a copy of that blueprint, and this copy is placed into the new machine, resulting in a faithful replication of the original machine.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Von_Neumann_universal_constructor

Drexler Nanofactory Replication System (1991-1992)
Following article shows the minimal structure of a cell that is required for self-replication to occur. It takes a lot of faith to believe, the cell could arise due to random natural chemical reactions.
Goals, Assumptions and Requirements
Goals:
Develop insights into internal design of the cell
Evaluate complexity in creating an artificial cell
Assumptions:
There is an intake of materials from the outside of cell
There is an output of waste materials from inside to outside of the cell
We assume throughout that we design for building an artificial cell – that need not have a biological basis (not built with carbon-based chemistry) but is rather a ‘clunky’ one (made from metal, plastic, semiconductors, etc.)
Requirements
The cell has an Enclosure to separate it and protect it from its environment
The cell is capable to create an identical copy of itself
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dCqb_hyFHEA
The Simplest Self-Replicator ( Cell ) Schematic Illustration

What happens during cell replication? – the “cloning” phase

What happens during cell replication? – the “division” phase

What would have to happen during the replication of our artifical cell ?
Input materials processed through material extraction into good materials for fabrication of parts or for energy generation
Energy is generated and made available throughout the cell
Fabrication function starts to fabricate parts, components and assemblies for:
Cloning (creating copies) of all cell internal elements
Creating scaffolding elements for the growing cell interior
Creating new elements that are added to the growing enclosure
When the cloning of all original cell internal parts completed, the cell division starts:
The original cell content is now at (for example) “north pole” of the cell enclosure
The cloned cell content (the “nascent daughter cell”) is now at the “south pole” of the cell enclosure
The SSR enclosure and its content now divides at the “equatorial” plane and the separate “mother” (at North) and daughter (at South) cell emerge.
Now lets say someone would decide to try to make a artifical cell, how would it be able to clone accurately all its internal parts?
It would not be possible by using a mechanical copy process – similar with that used to duplicate house keys. Using internal design information would be required in combination with computer controlled roboters.

Control of Input Flow, Functions of Material Identification and Material Extraction
Input Flow Control function
Opens/closes the enclosure input gateways
Acts based on the nature of input material/part and commands from other functions
Material and Parts Identification function
Identifies nature of input materials and parts
Tags input materials and parts, manufactured materials and fabricated parts with type Id (bar code like)
Material Extraction function
Uses specific processes to extract manufacturing materials from raw materials
Uses specific machinery and parts
Input Flow Control Function
Our cell needs to have gates which permit material to get in or out. Further it needs to be able to recognize and identify what the incoming materials in are made of. So the cell must be able to act like a roboter, programmed and automatically, by itself, to recognize the materials and permit or refuse their entrance.
Function of Energy Generation and internal transport highways and transport vessels
The cell needs to be able to generate energy from raw or processed materials. It needs to be able to transport and distribute materials, and managing energy requirements
( electricity ) It has to use special machinery: generators, transformers, converters.
An open question is, what material basis to provide energy: fuel, oil, coal, chemical, atomic etc.
Transport function:
Transport materials and parts/components
Uses containers, conduits, wires, carriers
Transports also energy and information
Ability of chain supply, recycling and function of output Flow control
Supply Chain function:
Ensures steady supply of materials, energy and parts
Coordinating and scheduling capability
Recycling function:
Re-introduce useful materials and parts in the fabrication cycle
Selects materials and parts as refuse; cleans spaces
Output Flow Control function:
Sends refuse materials and parts outside the cell
Controls output gateways of the enclosure
Storage of a catalog of all materials , Construction Plan , registration of construction status
Bill of Materials function:
Catalogs of all materials and all parts
For each element: its composition in sub-elements and materials
Construction Plan function:
Catalog of construction plan and design of all parts, components, assemblies including the cell as a whole
Catalog of all processes
Catalog of all procedures
Construction Status function:
Uses replicas of construction plans to mark construction progress
Status updated by functions involved in fabrication and construction
Hability of Manipulation , Fabrication of all parts, and Fabrication quality Control
Manipulation function:
Ability to “grab”, “handle”, “manipulate” materials, parts, components
Implemented with robot arm – like machinery
Fabrication Function:
Must be able to fabricate any and all cell parts and components
In particular able to fabricate all cell machinery
Fabrication Control function:
Follows the construction plans
Commands the fabrication function to manufacture next elements in the plan
Function of Communication and Notification, Growth Function through scaffolding and Enclosure Growth
Communication and Notification function:
Facilitates communication between the “control” centers and “execution” centers
Notifications from “executor” to “controller”
Scaffolding Growth function:
Controls construction and growth of cell scaffolding
Mostly on the “daughter” cell side
Enclosure Growth function:
Controls the construction and growth of the enclosure
Addition of enclosure gateways; flexible geometry
Cloning Function, Hability of cell Division and Replication
Cloning function
Choreographs the cloning phase
Coordinates fabrication of the clone and growth of scaffolding and enclosure
Copies info catalogs and software into the cloned parts
Division function:
Choreograph the cell division phase
“start the engines” of the “daughter” cell just before division completes
Replication function:
Highest level function:
Implements the designer commandments:
- Grow and
- Multiply
What we learned about the artificial Cell?
The cell must be designed for growth and division: the enclosure must support changing surface, volume and shape
The cell must contain detailed, structured, cohesive descriptive information that must be accurately and integrally passed to next cell generation.
Required information:
-all used materials: identification, description, characteristics
-manufacturing materials: extraction procedures and processes
-bill of materials for all fabricated parts, components and assemblies
-procedures and processes for energy generation, storage (if needed) transportation and management
-construction plans for all fabricated parts, components and assemblies including the cell itself.
-all fabrication processes and procedures
-all assemblage procedures
-all recycling procedures and processes
The cell
must contain advanced materials and parts identification capabilities as well as material extraction capabilities
must contain sophisticated, fully automated and computer-controlled capabilities for energy generation, transportation, management and distribution
must contain very sophisticated fabrication and assemblage capabilities that must be information-driven for full automation and computer control.
must posses advanced computing (information processing) capabilities as well as good information communication capabilities.
must control its many parts and layered functions through very advanced software running on cell-computer(-like) machinery.
Above all: the cell must be based on a very sophisticated design that harmoniously, precisely and completely provides full automation and self-sufficiency for all machinery and processes that happens inside an cell during its growth, division and replication.
The design of a cell can be successful only if it is harmoniously integrated and precisely coordinated with the design and characteristics of its environment.
An artificial cell most probable must contain:
a material mining sub-unit
a metallurgic subunit
a chemical plant
a power plant
an electricity distribution network
a network of avenues, alleys and conduits for robotized transportation
a semiconductor manufacturing plant
a computer manufacturing plant
an extended communication network connecting by wire or rather wirelessly all plants and robots
a software manufacturing plant and software distribution and installation agents.
a materials and parts recycling and refuse management plant
an army of intelligent robots for transportation and manipulation
a highly sophisticated distributed, multi-layered software system that controls in a cohesive manner all plants, robots and communications.

Robots made of classical components can make identical copies of themselves, but quantum machines can't.
Evaluating the Complexity of an artificial cell
The Cell: autonomous, computerized and automated
There is no comparable human engineering artifact in terms of:
Autonomy (materials, energy, fabrication closure, information closure, ‘intelligence’)
full manufacturing automation
spectrum of processes and fabrication types
No successful attempt so far on building a real autonomous artificial cell from scratch
Attempts so far:
software simulations
cellular automata
self-replicating software entities
RepRap – self replicating 3D printers
self-assembling Lego robots
Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS)
Craig Venter’s synthetic bacterial cell
Comparing a genuine artificial Cell with:
An advanced car manufacturing/assembly line:
many/most parts are fabricated elsewhere
not fully automated; many manual operations performed by humans
no material identification, material extraction capabilities
not so many process technologies involved
mostly an assembly operation
The Large Hadron Collider (HDC) in Switzerland
no fabrication
not comparable in terms of automation, process diversity
The Martian Rover
some good amount of autonomy
no fabrication
The Metaphysics of It All
A reasonable scientific hypothesis is that the Master Designer designed wisely all life types for this successful cohabitation of Homo Sapiens
with all other types of life.
More so it is hypothesized (again scientifically) that the Earth, the Solar System, the Milky Way Galaxy and the Whole Universe was designed and finely adjusted by the Master Designer so that Homo Sapiens and all other life forms have a comfortable and enjoyable place to live.
More so, besides having a comfortable place to live Homo Sapiens have plenty of cell types to study and to marvel at the fabulous skills of the Master Designer revealed so blatantly in His cell designs.
More so, besides having amazing engineering feats to discover and admire, the Homo Sapiens has a rightful Master Designer to praise and worship all his life.
A number of researchers have concluded that the spontaneous origin of life cannot be explained by known laws of physics and chemistry. Many seek “new” laws which can account for life’s origin. Why are so many unwilling to simply accept what the evidence points to: that the theory of evolution itself is fundamentally implausible? Dean Kenyon answers, “Perhaps these scientists fear that acceptance of this conclusion would leave open the possibility (or the necessity) of a supernatural origin of life” (p.viii).
1
If an atheist dismisses it out hand, it is either because he has not thought seriously about the huge task and difficulty required to make a first living self-replicating cell and why natural mechanisms are inadequate. Or he is committed to his naturalistic worldview in a way, that he is unwilling or incapable of recognizing the flaws of his worldview and convictions. In that case, only a miracle to change his mind. But a conversion is always a miracle, anyway..... Infront of the powerful facts and extraordinary requirements to make a self-replicating machine exposed, any argument brought forward by atheists is like dim and helpless excuses in order to reject an intelligent designer. Not based on scientific eloquent arguments, but wishful and obscured thinking, and bad will.
1) http://www.cogmessenger.org/wp-content/uploads/2013/06/Mystery_of_Life_Origin.pdf
2. ORIGINS AND EVOLUTION OF LIFE An Astrobiological Perspective MURIEL GARGAUD, page 58
Last edited by Admin on Tue Mar 03, 2020 8:04 am; edited 28 times in total

