Histones function and design
https://reasonandscience.catsboard.com/t2050-histones-function-and-design
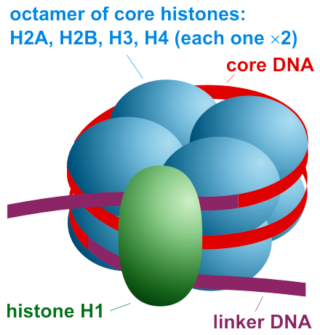
In biology, histones are highly alkaline proteins found in eukaryotic cell nuclei that package and order the DNA into structural units called nucleosomes.They are the chief protein components of chromatin, acting as spools around which DNA winds, and play a role in gene regulation. Without histones, the unwound DNA in chromosomes would be very long (a length to width ratio of more than 10 million to 1 in human DNA). For example, each human cell has about 1.8 meters of DNA, (~6 ft) but wound on the histones it has about 90 micrometers (0.09 mm) of chromatin, which, when duplicated and condensed during mitosis, result in about 120 micrometers of chromosomes
Question: How did natural processes "figure out" to condense DNA into such an enormously tiny, highly regulated and functional structure? Why at all should they do that?
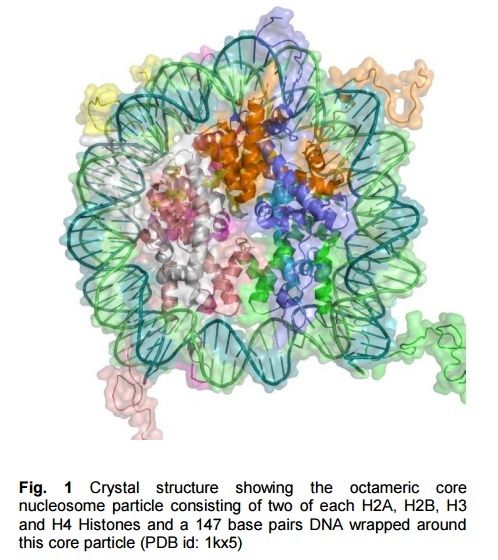

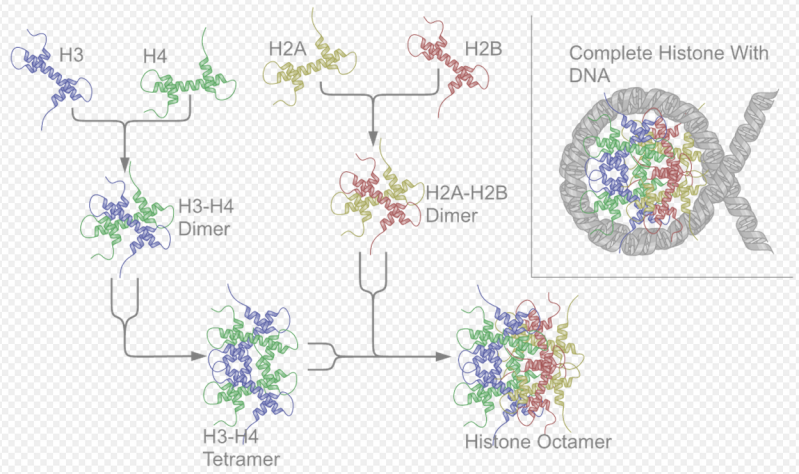
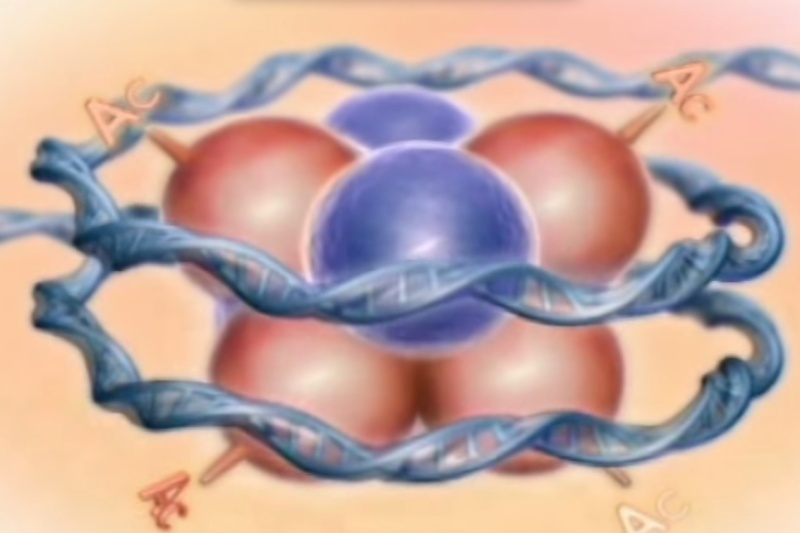
Histones are the major structural proteins of chromosomes. The DNA molecule is wrapped twice around a Histone Octamer to make a Nucleosome. Six Nucleosomes are assembled into a Solenoid in association with H1 histones. The solenoids are in turn coiled onto a Scaffold, which is futher coiled to make the chromosomal matrix.

Histone acetyltransferases (HATs)
Histone acetyltransferases (HATs) are enzymes that acetylate conserved lysine amino acids on histone proteins by transferring an acetyl group from acetyl CoA to form ε-N-acetyllysine. DNA is wrapped around histones, and, by transferring an acetyl group to the histones, genes can be turned on and off. In general, histone acetylation increases gene expression.
In general, histone acetylation is linked to transcriptional activation and associated with euchromatin. When it was first discovered, it was thought that acetylation of lysine neutralizes the positive charge normally present, thus reducing affinity between histone and (negatively charged) DNA, which renders DNA more accessible to transcription factors. Research has emerged, since, to show that lysine acetylation and other posttranslational modifications of histones generate binding sites for specific protein–protein interaction domains, such as the acetyllysine-binding bromodomain.[citation needed] Histone acetyltransferases can also acetylate non-histone proteins, such as nuclear receptors and other transcription factors to facilitate gene expression.
Histone deacetylase ( HDAC )
Histone deacetylases are a class of enzymes that remove acetyl groups (O=C-CH3) from an ε-N-acetyl lysine amino acid on a histone, allowing the histones to wrap the DNA more tightly. This is important because DNA is wrapped around histones, and DNA expression is regulated by acetylation and de-acetylation. Its action is opposite to that of histone acetyltransferase. HDAC proteins are now also called lysine deacetylases (KDAC), to describe their function rather than their target, which also includes non-histone proteins.
http://darwins-god.blogspot.com.br/2012/12/how-evolutionists-stole-histones.html
https://reasonandscience.catsboard.com/t2050-histones-function-and-design
In biology, histones are highly alkaline proteins found in eukaryotic cell nuclei that package and order the DNA into structural units called nucleosomes.They are the chief protein components of chromatin, acting as spools around which DNA winds, and play a role in gene regulation. Without histones, the unwound DNA in chromosomes would be very long (a length to width ratio of more than 10 million to 1 in human DNA). For example, each human cell has about 1.8 meters of DNA, (~6 ft) but wound on the histones it has about 90 micrometers (0.09 mm) of chromatin, which, when duplicated and condensed during mitosis, result in about 120 micrometers of chromosomes
Question: How did natural processes "figure out" to condense DNA into such an enormously tiny, highly regulated and functional structure? Why at all should they do that?


Histones are the major structural proteins of chromosomes. The DNA molecule is wrapped twice around a Histone Octamer to make a Nucleosome. Six Nucleosomes are assembled into a Solenoid in association with H1 histones. The solenoids are in turn coiled onto a Scaffold, which is futher coiled to make the chromosomal matrix.




Histone acetyltransferases (HATs)
Histone acetyltransferases (HATs) are enzymes that acetylate conserved lysine amino acids on histone proteins by transferring an acetyl group from acetyl CoA to form ε-N-acetyllysine. DNA is wrapped around histones, and, by transferring an acetyl group to the histones, genes can be turned on and off. In general, histone acetylation increases gene expression.
In general, histone acetylation is linked to transcriptional activation and associated with euchromatin. When it was first discovered, it was thought that acetylation of lysine neutralizes the positive charge normally present, thus reducing affinity between histone and (negatively charged) DNA, which renders DNA more accessible to transcription factors. Research has emerged, since, to show that lysine acetylation and other posttranslational modifications of histones generate binding sites for specific protein–protein interaction domains, such as the acetyllysine-binding bromodomain.[citation needed] Histone acetyltransferases can also acetylate non-histone proteins, such as nuclear receptors and other transcription factors to facilitate gene expression.
Histone deacetylase ( HDAC )
Histone deacetylases are a class of enzymes that remove acetyl groups (O=C-CH3) from an ε-N-acetyl lysine amino acid on a histone, allowing the histones to wrap the DNA more tightly. This is important because DNA is wrapped around histones, and DNA expression is regulated by acetylation and de-acetylation. Its action is opposite to that of histone acetyltransferase. HDAC proteins are now also called lysine deacetylases (KDAC), to describe their function rather than their target, which also includes non-histone proteins.
http://darwins-god.blogspot.com.br/2012/12/how-evolutionists-stole-histones.html
Last edited by Admin on Tue Nov 27, 2018 7:29 am; edited 6 times in total