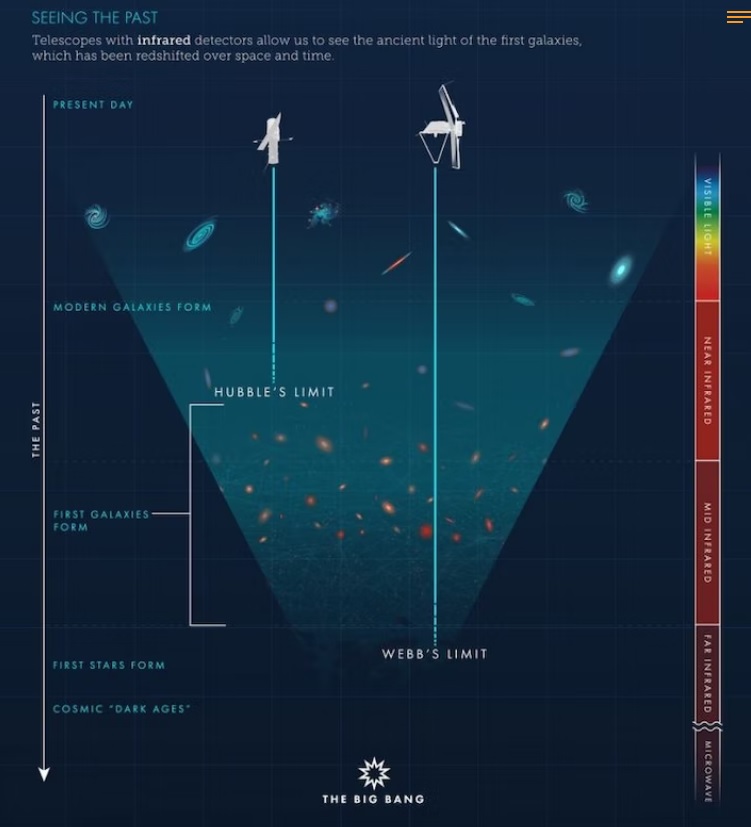
The Paradox: Grown-up Galaxies in an Infant Universe
https://reasonandscience.catsboard.com/t3091-the-paradox-grown-up-galaxies-in-an-infant-universe
Big Bang cosmology predicts that galaxies evolve over long periods of time: If galaxies were all formed long ago, distant galaxies should look younger than those nearby because light from them requires a longer time to reach us. Such galaxies should contain more short-lived stars and more gas out of which future generations of stars will form.
https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/the-evolution-of-the-universe/
The Genesis model, where God "stretched out" the heavens and created a "mature" universe, (in the same sense as he created Adam looking "mature" and grown up, even after being created instants ago), predicts ensembles of galaxies close to us should look statistically the same as those far away.
And that is what is being observed through the new J.Webb telescope.
Creation Cosmology Confirmed!
by Dr. Lisle | Sep 9, 2022 | Astronomy, Origins
https://biblicalscienceinstitute.com/origins/creation-cosmology-confirmed/
I asked Ethan Siegel ( He writes frequently in Forbes magazine, great articles btw.) what it means to find fully developed and grown galaxies close to the Big bang with the James Webb telescope:
He answered two things: 1. They have already found galaxies that are fully grown up, 600 Mio light years from the Big bang, and
2. Scientists did not expect ( or predict ) this, and there is no scientific answer.
Well. Maybe.... we have an answer
This might be the most important scientific news in our generation, with astonishing consequences in regard to science, philosophy, and worldviews. It will make a naturalistic claim for the origin of our universe MUCH more difficult - and confirm Genesis 1.
In the beginning, God created the heavens and the earth.
Zechariah 12:1
The LORD, who stretches out the heavens, who lays the foundation of the earth, and who forms the human spirit within a person
Science, once again, moving forward with new evidence at hand, corroborates the Bible !! Romans 3:4
Let God be true, and every human being a liar.
Panic! The Big Bang didn't happen
What do the James Webb images really show?
Panic! At the Disks: First Rest-frame Optical Observations of Galaxy Structure at z>3 with JWST in the SMACS 0723 Field
https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.09428
Our key findings are:
I. The morphological types of galaxies changes less quickly than previously believed, based on precursor HST imaging and results. That is, these early JWST results suggest that the formation of normal galaxy structure was much earlier than previously thought.
II. A major aspect of this is our discovery that disk galaxies are quite common at z > 3 − 6, where they make up ∼ 50% of the galaxy population, which is over 10 times as high as what was previously thought to be the case with HST observations. That is, this epoch is surprisingly full of disk galaxies, which observationally we had not been able to determine before JWST.
III. Distant galaxies at z > 3 in the rest-frame optical, despite their appearance in the HST imaging, are not as highly clumpy and asymmetric as once thought. This effect has not been observed before due to the nature of existing deep imaging with the HST which could probe only ultraviolet light at z > 3. This shows the great power of JWST to probe rest-frame optical where the underlying mass of galaxies can now be traced and measured.
Why do the JWST’s images inspire panic among cosmologists? And what theory’s predictions are they contradicting? The papers don’t actually say. The truth that these papers don’t report is that the hypothesis that the JWST’s images are blatantly and repeatedly contradicting is the Big Bang Hypothesis that the universe began 14 billion years ago in an incredibly hot, dense state and has been expanding ever since. Since that hypothesis has been defended for decades as unquestionable truth by the vast majority of cosmological theorists, the new data is causing these theorists to panic. “Right now I find myself lying awake at three in the morning,” says Alison Kirkpatrick, an astronomer at the University of Kansas in Lawrence, “and wondering if everything I’ve done is wrong.”
The galaxies that the JWST shows are just the same size as the galaxies near to us, assuming that the universe is not expanding and redshift is proportional to distance.
https://iai.tv/articles/the-big-bang-didnt-happen-auid-2215?_auid=2020
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yAhvuii41RE
Dr. Danny R. Faulkner on August 9, 2022 :A more recent study claimed to identify a galaxy so far away that it dates to only 200 million years after the big bang.2 If astronomers accept these distances and ages, then it will require extensive rewriting of their understanding of galaxy formation and early evolution, as well as the formation of stars.
https://answersingenesis.org/astronomy/james-webb-space-telescope-distant-galaxies/
YEC view should predict that we will find more and more distant galaxies, fully developed.
Mark Corbett:
1. Will show similar amounts of rotation and development of spiral shapes as nearby galaxies on average
2. Will have similar levels of dust and metallicity as nearby galaxies on average
3. The stars will be on average similar rather than having a higher portion of larger, bluer, hotter, faster burning stars
4. The galaxies on average will be similar in size
The earliest galaxies in the universe are commonly thought to have been much smaller associations of stars that gradually merged to build large galaxies like our Milky Way.. But, among the most distant galaxies ever seen, they appears to be unusually massive and mature for its place in the young universe. This came as a surprise to astronomers. While astronomers generally believe most galaxies were built piecewise by mergers of smaller galaxies, the discovery of this object suggests at least a few galaxies formed quickly long ago. For such a large galaxy, this would have been a tremendously explosive event of star birth.
https://www.nasa.gov/vision/universe/starsgalaxies/spitzer-20050927.html
My comment: For a believer that God created the universe and the earth in six days, this comes not to a surprise. God created everything fully ready from the get go.
Peering deep into the Universe we see objects as there were when the light first left them. Images such as the Hubble Ultra Deep Field show that huge numbers of galaxies of all sizes had grown surprisingly quickly in the early Universe.
https://theconversation.com/baby-galaxies-light-up-the-universe-72860
An Old-looking Galaxy in a Young Universe
One of the most distant galaxies ever observed has provided astronomers with the first detection of dust in such a remote star-forming system and tantalising evidence for the rapid evolution of galaxies after the Big Bang. The new observations have used ALMA to pick up the faint glow from cold dust in the galaxy A1689-zD1 and used ESO’s Very Large Telescope to measure its distance.
https://www.eso.org/public/news/eso1508/
Galaxies in the infant universe were surprisingly mature
Largest survey yet of distant galaxies in the early universe “Massive galaxies were already much more mature in the early universe than previously expected. This was shown by an international team of astronomers who studied 118 distant galaxies with the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA).”
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2020/10/201027105426.htm
The ALPINE-ALMA [CII] survey Dust attenuation properties and obscured star formation at z ∼4.4–5.8
https://sci-hub.ren/10.1051/0004-6361/202038163
Massive Galaxies in Early Universe were More Mature than Previously Thought October 27, 2020
Galaxies are considered more ‘mature’ than ‘primordial’ when they contain a significant amount of dust and heavy elements — by-products of dying stars. But galaxies in the early Universe have not had much time to build stars yet, so astronomers don’t expect to see much dust or heavy elements there either. “To our surprise, many of them were much more mature than we had expected,”
[url=http://www.sci-news.com/astronomy/mature-massive-galaxies-early-universe- 08992.html]http://www.sci-news.com/astronomy/mature-massive-galaxies-early-universe- 08992.html[/url]
This finding contravenes current models [underline added] for that period of cosmic evolution 2019
"The existence of these large number of massive and dusty galaxies is unexpected in
current models or simulations, which shows that the Universe can form massive
systems more efficiently in the early times than we thought," Tao Wang
https://sci-hub.ren/10.1038/s41586-019-1452-4
"This finding contravenes current models [underline added] for that period of cosmic evolution and will help to add some details, which have been missing until now." Tao Wang
https://www.sciencealert.com/astronomers-have-just-found-some-of-the-earlyuniverses-missing-galaxies
ESO (European Southern Observatory): An Old-looking Galaxy in a Young Universe
“They were surprised to discover a far more evolved system than expected. It had a fraction of dust similar to a very mature galaxy, such as the Milky Way.”
https://www.eso.org/public/usa/news/eso1508/
National Geographic: Astronomers Find a Dusty Galaxy That Shouldn't Exist
https://www.nationalgeographic.com/news/2015/2/150302-black-hole-blastbiggest-science-galaxies-space/
The Paradox: Grown-up Galaxies in an Infant Universe (NASA - December 1994)
“The surprise is that elliptical galaxies appeared remarkably "normal" when the universe was a fraction of its current age, meaning that they must have formed a short time after the Big Bang… The surprise is that elliptical galaxies appeared remarkably "normal" when the universe was a fraction of its current age, meaning that they must have formed a short time after the Big Bang.”
https://hubblesite.org/contents/news-releases/1994/news-1994-52.html
Rare Grand-Design Spiral Galaxy at Redshift z = 2.18 (19 July 2012);
“The fact that this galaxy exists is astounding,” Law said. “Current wisdom holds that such grand design spiral galaxies didn't exist at such an early time in the history of the universe.” D.R. Law
https://sci-hub.ren/10.1038/nature11256
A dusty, normal galaxy in the epoch of reionization (Nature) (19 March 2015)
“Last week we learned of an incredibly massive black hole in the early universe. Now we have this average galaxy with significant amounts of dust. We've had this cartoon picture of the early universe, but it's clear that we really don't know what's going on.” (Daniel Marrone, University of Arizona)
https://www.nature.com/articles/nature14164?page=1
Water in the Early Universe 2011 November 10.
“… it is another demonstration that water is pervasive throughout the universe, even at the very earliest times.”
Matt Bradford NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory
https://www.nasa.gov/topics/universe/features/universe20110722.html
It sounds like Genesis 1:2 (… the Spirit of God hovering over the water in the beginning of God’s creation!)

https://reasonandscience.catsboard.com/t3091-the-paradox-grown-up-galaxies-in-an-infant-universe
Big Bang cosmology predicts that galaxies evolve over long periods of time: If galaxies were all formed long ago, distant galaxies should look younger than those nearby because light from them requires a longer time to reach us. Such galaxies should contain more short-lived stars and more gas out of which future generations of stars will form.
https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/the-evolution-of-the-universe/
The Genesis model, where God "stretched out" the heavens and created a "mature" universe, (in the same sense as he created Adam looking "mature" and grown up, even after being created instants ago), predicts ensembles of galaxies close to us should look statistically the same as those far away.
And that is what is being observed through the new J.Webb telescope.
Creation Cosmology Confirmed!
by Dr. Lisle | Sep 9, 2022 | Astronomy, Origins
https://biblicalscienceinstitute.com/origins/creation-cosmology-confirmed/
I asked Ethan Siegel ( He writes frequently in Forbes magazine, great articles btw.) what it means to find fully developed and grown galaxies close to the Big bang with the James Webb telescope:
He answered two things: 1. They have already found galaxies that are fully grown up, 600 Mio light years from the Big bang, and
2. Scientists did not expect ( or predict ) this, and there is no scientific answer.
Well. Maybe.... we have an answer
This might be the most important scientific news in our generation, with astonishing consequences in regard to science, philosophy, and worldviews. It will make a naturalistic claim for the origin of our universe MUCH more difficult - and confirm Genesis 1.
In the beginning, God created the heavens and the earth.
Zechariah 12:1
The LORD, who stretches out the heavens, who lays the foundation of the earth, and who forms the human spirit within a person
Science, once again, moving forward with new evidence at hand, corroborates the Bible !! Romans 3:4
Let God be true, and every human being a liar.
Panic! The Big Bang didn't happen
What do the James Webb images really show?
Panic! At the Disks: First Rest-frame Optical Observations of Galaxy Structure at z>3 with JWST in the SMACS 0723 Field
https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.09428
Our key findings are:
I. The morphological types of galaxies changes less quickly than previously believed, based on precursor HST imaging and results. That is, these early JWST results suggest that the formation of normal galaxy structure was much earlier than previously thought.
II. A major aspect of this is our discovery that disk galaxies are quite common at z > 3 − 6, where they make up ∼ 50% of the galaxy population, which is over 10 times as high as what was previously thought to be the case with HST observations. That is, this epoch is surprisingly full of disk galaxies, which observationally we had not been able to determine before JWST.
III. Distant galaxies at z > 3 in the rest-frame optical, despite their appearance in the HST imaging, are not as highly clumpy and asymmetric as once thought. This effect has not been observed before due to the nature of existing deep imaging with the HST which could probe only ultraviolet light at z > 3. This shows the great power of JWST to probe rest-frame optical where the underlying mass of galaxies can now be traced and measured.
Why do the JWST’s images inspire panic among cosmologists? And what theory’s predictions are they contradicting? The papers don’t actually say. The truth that these papers don’t report is that the hypothesis that the JWST’s images are blatantly and repeatedly contradicting is the Big Bang Hypothesis that the universe began 14 billion years ago in an incredibly hot, dense state and has been expanding ever since. Since that hypothesis has been defended for decades as unquestionable truth by the vast majority of cosmological theorists, the new data is causing these theorists to panic. “Right now I find myself lying awake at three in the morning,” says Alison Kirkpatrick, an astronomer at the University of Kansas in Lawrence, “and wondering if everything I’ve done is wrong.”
The galaxies that the JWST shows are just the same size as the galaxies near to us, assuming that the universe is not expanding and redshift is proportional to distance.
https://iai.tv/articles/the-big-bang-didnt-happen-auid-2215?_auid=2020
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yAhvuii41RE
Dr. Danny R. Faulkner on August 9, 2022 :A more recent study claimed to identify a galaxy so far away that it dates to only 200 million years after the big bang.2 If astronomers accept these distances and ages, then it will require extensive rewriting of their understanding of galaxy formation and early evolution, as well as the formation of stars.
https://answersingenesis.org/astronomy/james-webb-space-telescope-distant-galaxies/
YEC view should predict that we will find more and more distant galaxies, fully developed.
Mark Corbett:
1. Will show similar amounts of rotation and development of spiral shapes as nearby galaxies on average
2. Will have similar levels of dust and metallicity as nearby galaxies on average
3. The stars will be on average similar rather than having a higher portion of larger, bluer, hotter, faster burning stars
4. The galaxies on average will be similar in size
The earliest galaxies in the universe are commonly thought to have been much smaller associations of stars that gradually merged to build large galaxies like our Milky Way.. But, among the most distant galaxies ever seen, they appears to be unusually massive and mature for its place in the young universe. This came as a surprise to astronomers. While astronomers generally believe most galaxies were built piecewise by mergers of smaller galaxies, the discovery of this object suggests at least a few galaxies formed quickly long ago. For such a large galaxy, this would have been a tremendously explosive event of star birth.
https://www.nasa.gov/vision/universe/starsgalaxies/spitzer-20050927.html
My comment: For a believer that God created the universe and the earth in six days, this comes not to a surprise. God created everything fully ready from the get go.
Peering deep into the Universe we see objects as there were when the light first left them. Images such as the Hubble Ultra Deep Field show that huge numbers of galaxies of all sizes had grown surprisingly quickly in the early Universe.
https://theconversation.com/baby-galaxies-light-up-the-universe-72860
An Old-looking Galaxy in a Young Universe
One of the most distant galaxies ever observed has provided astronomers with the first detection of dust in such a remote star-forming system and tantalising evidence for the rapid evolution of galaxies after the Big Bang. The new observations have used ALMA to pick up the faint glow from cold dust in the galaxy A1689-zD1 and used ESO’s Very Large Telescope to measure its distance.
https://www.eso.org/public/news/eso1508/
Galaxies in the infant universe were surprisingly mature
Largest survey yet of distant galaxies in the early universe “Massive galaxies were already much more mature in the early universe than previously expected. This was shown by an international team of astronomers who studied 118 distant galaxies with the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA).”
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2020/10/201027105426.htm
The ALPINE-ALMA [CII] survey Dust attenuation properties and obscured star formation at z ∼4.4–5.8
https://sci-hub.ren/10.1051/0004-6361/202038163
Massive Galaxies in Early Universe were More Mature than Previously Thought October 27, 2020
Galaxies are considered more ‘mature’ than ‘primordial’ when they contain a significant amount of dust and heavy elements — by-products of dying stars. But galaxies in the early Universe have not had much time to build stars yet, so astronomers don’t expect to see much dust or heavy elements there either. “To our surprise, many of them were much more mature than we had expected,”
[url=http://www.sci-news.com/astronomy/mature-massive-galaxies-early-universe- 08992.html]http://www.sci-news.com/astronomy/mature-massive-galaxies-early-universe- 08992.html[/url]
This finding contravenes current models [underline added] for that period of cosmic evolution 2019
"The existence of these large number of massive and dusty galaxies is unexpected in
current models or simulations, which shows that the Universe can form massive
systems more efficiently in the early times than we thought," Tao Wang
https://sci-hub.ren/10.1038/s41586-019-1452-4
"This finding contravenes current models [underline added] for that period of cosmic evolution and will help to add some details, which have been missing until now." Tao Wang
https://www.sciencealert.com/astronomers-have-just-found-some-of-the-earlyuniverses-missing-galaxies
ESO (European Southern Observatory): An Old-looking Galaxy in a Young Universe
“They were surprised to discover a far more evolved system than expected. It had a fraction of dust similar to a very mature galaxy, such as the Milky Way.”
https://www.eso.org/public/usa/news/eso1508/
National Geographic: Astronomers Find a Dusty Galaxy That Shouldn't Exist
https://www.nationalgeographic.com/news/2015/2/150302-black-hole-blastbiggest-science-galaxies-space/
The Paradox: Grown-up Galaxies in an Infant Universe (NASA - December 1994)
“The surprise is that elliptical galaxies appeared remarkably "normal" when the universe was a fraction of its current age, meaning that they must have formed a short time after the Big Bang… The surprise is that elliptical galaxies appeared remarkably "normal" when the universe was a fraction of its current age, meaning that they must have formed a short time after the Big Bang.”
https://hubblesite.org/contents/news-releases/1994/news-1994-52.html
Rare Grand-Design Spiral Galaxy at Redshift z = 2.18 (19 July 2012);
“The fact that this galaxy exists is astounding,” Law said. “Current wisdom holds that such grand design spiral galaxies didn't exist at such an early time in the history of the universe.” D.R. Law
https://sci-hub.ren/10.1038/nature11256
A dusty, normal galaxy in the epoch of reionization (Nature) (19 March 2015)
“Last week we learned of an incredibly massive black hole in the early universe. Now we have this average galaxy with significant amounts of dust. We've had this cartoon picture of the early universe, but it's clear that we really don't know what's going on.” (Daniel Marrone, University of Arizona)
https://www.nature.com/articles/nature14164?page=1
Water in the Early Universe 2011 November 10.
“… it is another demonstration that water is pervasive throughout the universe, even at the very earliest times.”
Matt Bradford NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory
https://www.nasa.gov/topics/universe/features/universe20110722.html
It sounds like Genesis 1:2 (… the Spirit of God hovering over the water in the beginning of God’s creation!)

Last edited by Otangelo on Sun Sep 25, 2022 10:03 am; edited 2 times in total