Proteome of a Minimal Cell Required for LifeThe proteome of a minimal cell essential for life is comprised of a network of proteins and enzymes that are fundamental for metabolic processes, energy production, and cellular maintenance. These proteins serve as the building blocks for a variety of biochemical pathways, each playing an essential role in sustaining life. From energy production to DNA replication, the components of this minimal proteome reflect a system that is highly efficient and finely regulated. The sheer number and variety of enzymes involved in these pathways highlight the complexity and precision required for even the most basic cellular functions. The detailed interactions between enzymes, cofactors, and substrates form an interdependent network that must function seamlessly. The listed proteome represents a highly plausible minimal set of proteins necessary for a free-living organism. It reflects the core biochemical processes essential for independent life, and its similarity in size and content to *Pelagibacter ubique* underscores the relevance of such a model in understanding life’s minimal requirements.
1. Metabolism and Energy Production 1. Glycolysis enzyme group (10 enzymes): 3,202 amino acids
2. Gluconeogenesis enzyme group (4 enzymes): 2,407 amino acids
3. Oxidative phase enzyme group (3 enzymes): 1,177 amino acids
4. Non-oxidative phase enzyme group (4 enzymes): 1,376 amino acids
5. Nucleotide group (3 enzymes): 1,189 amino acids
6. THF derivative-related essential enzyme group (4 enzymes): 793 amino acids
7. CO₂ reduction pathway enzyme group (6 enzymes): 2,403 amino acids
8. Acetyl-CoA-related essential enzyme group (2 enzymes): 1,269 amino acids
9. Methylamine reduction pathway enzyme group (5 enzymes): 2,157 amino acids
10. Methanogenesis-related essential enzyme group (1 enzyme): 593 amino acids
11. Pyruvate metabolism-related enzyme group (6 enzymes): 4,135 amino acids
12. NADH dehydrogenase Complex I-related essential enzyme group (14 subunits): 4,800 amino acids
13. Succinate dehydrogenase and hydrogenase enzyme group (6 enzymes): 1,750 amino acids
14. Cytochrome bc1 complex III enzyme group (3 subunits): 800 amino acids
Total number of enzymes/proteins: 61 Total number of amino acids: 27,0512. Electron Transport and ATP Synthesis 1. Cytochrome c oxidase complex (3 subunits): 970 amino acids
2. ATP Synthase Complex V enzyme group (9 subunits): 2,109 amino acids
3. Alternative electron transport and metabolic enzyme group (7 enzymes): 2,942 amino acids
4. Citric Acid Cycle enzyme group (8 enzymes): 3,965 amino acids
5. rTCA cycle enzyme group (4 enzymes): 2,474 amino acids
6. Beta-alanine biosynthesis essential enzyme group (1 enzyme): 110 amino acids
7. NAD⁺ biosynthesis enzyme group (8 enzymes): 2,217 amino acids
8. Flavin-related essential enzyme group (4 enzymes): 856 amino acids
9. NAD+ transporter group (2 transporters): 689 amino acids
10. Nitrogenase complex and associated energy delivery proteins (4 enzyme systems): 3,262 amino acids
11. Minimal enzyme group for functional nitrogen fixation and assimilation (4 enzymes): 3,128 amino acids
12. Enzyme group related to phosphonate and phosphinate metabolism (12 enzymes): 3,810 amino acids
13. Lysine biosynthesis pathway via diaminopimelate (6 enzymes): 2,001 amino acids
Total number of enzymes/proteins: 72 Total number of amino acids: 28,5333. Redox and Sulfur Metabolism 1. Redox enzyme group (3 enzymes): 1,293 amino acids
2. Sulfur metabolism pathway (7 enzymes): 2,190 amino acids
3. Oxidoreductase group involved in anaerobic metabolism and carbon fixation (5 enzymes): 3,108 amino acids
4. Tetrapyrrole biosynthesis enzyme group (5 enzymes): 1,732 amino acids
5. NAD+ salvage pathway enzyme group (5 enzymes): 1,371 amino acids
6. NAD+ transporter group (2 transporters): 689 amino acids
7. Methionine cycle and SAM/SAH metabolism enzyme group (3 enzymes): 1,356 amino acids
Total number of enzymes/proteins: 30 Total number of amino acids: 11,7394. Amino Acid Metabolism 1. Serine biosynthesis pathway (3 enzymes): 846-971 amino acids
2. Glycine cleavage system (4 enzymes): 1,933 amino acids
3. Glycine-serine interconversion and glycine cleavage system (5 enzymes): 2,331 amino acids
4. Direct conversion of serine and sulfide into cysteine (2 enzymes): 537 amino acids
5. Transsulfuration pathway (3 enzymes): 1,201 amino acids
6. Sulfur assimilation and cysteine biosynthesis pathway (7 enzymes): 2,291 amino acids
7. Alanine metabolism pathway (2 enzymes): 821 amino acids
8. Additional enzymes in alanine metabolism (3 enzymes): 1,119 amino acids
9. Valine biosynthesis pathway (4 enzymes): 1,692 amino acids
10. Leucine biosynthesis pathway (6 enzymes): 2,661 amino acids
11. Isoleucine biosynthesis pathway (5 enzymes): 2,132 amino acids
12. Histidine biosynthesis pathway (9 enzymes): 2,190 amino acids
13. Tryptophan biosynthesis pathway (5 enzymes): 1,590 amino acids
14. Tyrosine biosynthesis pathway (3 enzymes): 895 amino acids
15. Phenylalanine biosynthesis pathway (3 enzymes): 828 amino acids
16. Aspartate metabolism pathway (4 enzymes): 1,587 amino acids
17. Core of asparagine metabolism (2 enzymes): 847 amino acids
18. Methionine biosynthesis pathway (4 enzymes): 1,785 amino acids
19. Lysine biosynthesis enzyme group (6 enzymes): 1,640 amino acids
20. Threonine biosynthesis essential enzyme group (5 enzymes): 1,823 amino acids
21. Ornithine and proline metabolism essential enzyme group (5 enzymes): 1,632 amino acids
Total number of enzymes/proteins: 86 Total number of amino acids: 31,392-31,5175. Glutamate and Related Amino Acid Metabolism 1. Glutamate-related essential enzyme group (5 enzymes): 1,790 amino acids
2. Expanded glutamate-related essential enzyme group (9 enzymes): 3,251 amino acids
3. Ornithine and arginine biosynthesis essential enzyme group (4 enzymes): 1,564 amino acids
4. Ornithine and proline metabolism essential enzyme group (5 enzymes): 1,632 amino acids
5. Regulatory enzymes and proteins in amino acid synthesis (8 components): 4,169 amino acids
Total number of enzymes/proteins: 31 Total number of amino acids: 12,4066. Nucleotide Metabolism 1. De novo purine biosynthesis pathway (11 enzymes): 4,019 amino acids
2. De novo purine biosynthesis pathway enzyme group (leading to adenine) (4 enzymes): 1,751 amino acids
3. De novo purine biosynthesis pathway enzyme group (leading to guanine) (5 enzymes): 2,308 amino acids
4. De novo pyrimidine biosynthesis pathway (9 enzymes): 3,369 amino acids
5. De novo uracil biosynthesis pathway (6 enzymes): 2,884 amino acids
6. Cytosine nucleotide biosynthesis enzyme group (3 enzymes): 881 amino acids
7. De novo thymine biosynthesis pathway (4 enzymes): 1,288 amino acids
8. Nucleotide phosphorylation pathway (2 enzymes): 346 amino acids
9. Nucleotide Salvage enzyme group (4 enzymes): 1,985 amino acids
Total number of enzymes/proteins: 48 Total number of amino acids: 18,8317. Lipid Metabolism 1. Initiation of fatty acid synthesis enzyme group (3 enzymes): 5,147 amino acids
2. Fatty acid synthesis cycle enzyme group (5 enzyme domains): 1,379 amino acids
3. Termination and modification of fatty acid synthesis enzyme group (3 enzymes): 3,133 amino acids
4. Fatty acid elongation enzyme group (1 enzyme domain): 262 amino acids
5. Phospholipid biosynthesis enzyme group (2 enzymes): 563 amino acids
6. CDP-diacylglycerol synthesis enzyme group (1 enzyme): 243 amino acids
7. Phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylserine biosynthesis enzyme group (4 enzymes): 1,582 amino acids
8. Glycerophospholipid biosynthesis enzyme group (3 enzymes): 806 amino acids
9. Expanded glycerophospholipid biosynthesis enzyme group (3 enzymes): 1,044 amino acids
10. Additional enzyme group (2 enzymes): 2,389 amino acids
11. Phospholipid degradation enzyme group (4 enzymes): 1,140 amino acids
Total number of enzymes/proteins: 40 Total number of amino acids: 17,6888. Cofactor Metabolism 1. THF derivative-related essential enzyme group (4 enzymes): 793 amino acids
2. SAM synthesis enzyme group (4 enzymes): 1,161 amino acids
3. Methionine cycle and SAM/SAH metabolism enzyme group (3 enzymes): 1,356 amino acids
4. Methyl transfer and SAM-related enzyme group (2 components): 316 amino acids
5. Biotin biosynthesis essential enzyme group (4 enzymes): 1,329 amino acids
6. Thiamine biosynthesis enzyme group (4 enzymes): 1,417 amino acids
7. Wood-Ljungdahl pathway essential enzyme group (2 enzymes): 1,352 amino acids
8. One-carbon metabolism and formate oxidation pathway enzyme group (4 enzymes): 1,473 amino acids
9. Cobalamin biosynthesis enzyme group (30 enzymes): 7,720 amino acids
10. Cobalamin recycling enzyme group (4 enzymes): 2,412 amino acids
Total number of enzymes/proteins: 61 Total number of amino acids: 20,3299. DNA Replication and Repair 1. Bacterial DNA replication initiation process (11 key proteins): 1,096 amino acids
2. DNA replication initiation enzyme group (2 enzymes): 419 amino acids
3. DNA replication primase enzyme group (1 enzyme): 300 amino acids
4. DNA replication enzyme group (7 enzymes and proteins): 3,387 amino acids
5. DNA replication termination enzyme group (3 enzymes): 1,350 amino acids
6. Auxiliary DNA replication protein group (2 enzymes and proteins): 828 amino acids
7. DNA repair enzyme group (8 enzymes and proteins): 4,866 amino acids
8. Chromosome segregation and DNA modification enzyme group (2 enzymes): 1,513 amino acids
9. DNA mismatch and error recognition enzyme group (6 enzymes): 2,644 amino acids
10. DNA Topoisomerase enzyme group (1 enzyme): 589 amino acids
11. DNA Supercoiling Control enzyme group (5 components): 5,023 amino acids
12. DNA topology management and genetic exchange enzyme group (2 enzymes): 1,116 amino acids
13. DNA precursor synthesis enzyme group (4 enzymes): 1,152 amino acids
14. DNA precursor metabolism enzyme group (8 enzymes): 1,472 amino acids
Total number of enzymes/proteins: 72 Total number of amino acids: 25,75510. Transcription and RNA Processing 1. RNA polymerase enzyme group (5 enzymes): 2,550 amino acids
2. Transcription initiation factor group (5 enzymes): 1,541 amino acids
3. RNA Polymerase holoenzyme complex (11 subunits): 5,755 amino acids
4. Transcription factor group (4 example TFs): 954 amino acids
5. Additional transcription factor (1 TF): 209 amino acids
6. Repressor transcription factor group (2 examples): 468 amino acids
7. Expanded repressor transcription factor group (6 examples): 1,595 amino acids
8. Regulatory protein group (3 proteins): 778 amino acids
9. Sigma factor group (4 distinct types): 1,704 amino acids
10. Primary sigma factor group (1 type, σ70): 613 amino acids
11. Specific regulatory elements (2 types): 50-100 amino acids
12. Transcription termination enzyme group (4 enzymes): 1,199 amino acids
13. Transcription fidelity and repair enzyme group (6 enzymes): 6,950 amino acids
14. RNA Polymerase Subunit Diversity enzyme group (5 components): 4,553 amino acids
Total number of enzymes/proteins: 66 Total number of amino acids: 28,25911. Translation and Protein Synthesis 1. Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase enzyme group (18 enzymes): 9,703 amino acids
2. tRNA group (20 distinct types): 1,510 nucleotides
3. tRNA synthesis enzyme group (9 enzymes): 1,487 amino acids
4. tRNA Maturation enzyme (1 enzyme): 351 amino acids
5. Additional tRNA-related enzyme group (6 enzymes): 1,059 amino acids
6. tRNA modification and recycling group (6 enzymes): 1,168 amino acids
7. Translation Initiation protein group (3 proteins): 992 amino acids
8. Main rRNAs in prokaryotic ribosomes (3 rRNAs): 4,560 nucleotides
9. Ribosomal protein group in *E. coli* (21 proteins): 3,129 amino acids
10. Translation elongation factor group (2 factors): 1,097 amino acids
11. 50S ribosomal subunit protein group (33 proteins): 3,544 amino acids
12. Termination of protein synthesis enzyme group (3 enzymes): 1,184 amino acids
Total number of enzymes/proteins: 110 Total number of amino acids: 34,377 Total number of nucleotides: 6,07012. Ribosome Assembly and Quality Control 1. Early ribonucleotide synthesis enzyme group (18 enzymes and 2 factors): 6,000 amino acids
2. rRNA processing enzyme group (5 enzymes): 4,687 amino acids
3. Core enzyme group involved in 30S subunit assembly (6 enzymes): 3,826 amino acids
4. Ribosome assembly enzyme group (6 proteins): 4,450 amino acids
5. Ribosome Quality Control and Recycling protein group (4 proteins): 1,490 amino acids
6. Ribosome regulation group (9 key players): 2,696 amino acids
Total number of enzymes/proteins: 48 Total number of amino acids: 23,14913. Protein Folding, Modification, and Degradation 1. Protein folding and stability group (5 key players): 1,912 amino acids
2. Protein modification and processing enzyme group (6 enzymes): 1,341 amino acids
3. Protein targeting and translocation group (2 key players): 883 amino acids
4. Protein degradation group (4 enzymes): 1,433 amino acids
5. Post-translational modification enzyme group (2 enzymes): 363 amino acids
6. Biotin carboxyl-carrier protein ligase (1 protein): 214 amino acids
7. Aminopeptidase P (1 protein): 300 amino acids
Total number of enzymes/proteins: 21 Total number of amino acids: 6,44614. Ion Channels and Transporters 1. Ion Channel transporter group (12 enzymes and channels): 4,200 amino acids
2. P-Type ATPase group (7 enzymes): 5,900 amino acids
3. Metal ion transporter group (5 enzymes): 1,828 amino acids
4. Aquaporins (1 protein): 231 amino acids
5. Symporter and Antiporter group (6 transporters): 4,154 amino acids
6. ABC transporter group (3 transporters): 3,721 amino acids
7. Nutrient uptake transporter group (2 transporters): 801 amino acids
8. Sugar transporter group (5 transporter families): 2,086 amino acids
9. Carbon source transporter group (3 proteins): 1,357 amino acids
10. Co-factor transporter group (3 proteins): 787 amino acids
11. Nucleotide transporter and related enzyme group (5 key players): 897 amino acids
12. Hypothetical transporter group (1 type): 940 amino acids
13. Phosphate transporter group (5 types): 2,850 amino acids
14. Magnesium transporter and related system group (5 types): 1,450 amino acids
15. Amino acid transporter group (3 key players): 980 amino acids
16. Folate transporter group (3 key players): 1,201 amino acids
17. SAM transporter group (4 types): 1,825 amino acids
18. Fatty acid and precursor transporter group (2 types): 1,150 amino acids
Total number of enzymes/proteins: 90 Total number of amino acids: 40,45815. Cellular Machinery and Structural Components 1. Protein Export Machinery enzyme group (5 key components): 2,395 amino acids
2. Lipid transport and recycling enzyme group (6 enzymes): 2,757 amino acids
3. Secretion systems group (5 systems): 1,138 amino acids
4. Chromosome partitioning and segregation group (2 proteins): 935 amino acids
5. Cytokinesis enzyme group (4 key enzymes): 1,961 amino acids
6. Cell Wall or Membrane Synthesis enzyme group (7 enzymes): 2,239 amino acids
7. Distribution of Cellular Component protein group (4 proteins): 4,662 amino acids
8. Regulation and timing protein group (5 proteins): 1,847 amino acids
9. FtsZ protein group (4 proteins): 1,209 amino acids
10. Min protein group (4 proteins): 878 amino acids
11. DNA Management Proteins (NAPs) group (3 proteins): 1,848 amino acids
Total number of enzymes/proteins: 50 Total number of amino acids: 21,86916. RNA and Protein Quality Control 1. Prokaryotic rRNA synthesis and quality control pathway enzyme group (15 enzymes): 4,655 amino acids
2. Prokaryotic tRNA quality control enzyme group (17 enzymes): 5,000–6,000 amino acids
3. Prokaryotic rRNA modification, surveillance, and recycling enzyme group (6 proteins): 1,000–1,500 amino acids
4. Prokaryotic ribosomal protein quality control and error detection group (13 proteins): 3,750 amino acids
5. Ubiquitin-like Protein Modification enzyme group (4 enzymes): 1,047 amino acids
6. Prokaryotic error detection group in 30S assembly (4 proteins): 2,219 amino acids
7. 50S subunit error detection, repair, and recycling group (8 proteins): 3,201 amino acids
8. 70S ribosome assembly quality control and maintenance group (3 proteins): 1,065 amino acids
9. Quality control and recycling group in ribosome assembly (7 proteins): 2,497 amino acids
10. Regulation and quality control group in ribosome biogenesis (6 components): 2,406 amino acids
11. Comprehensive translation quality control system (10 key enzyme groups): 4,607 amino acids
12. Chiral checkpoint enzyme group (5 enzymes): 1,415 amino acids
13. Ribosome recycling and quality control enzyme group (5 enzymes): 2,117 amino acids
14. Post-translation quality control enzyme group (5 enzymes): 3,234 amino acids
15. Proteolysis pathway enzyme group (3 key enzymes): 1,215 amino acids
16. Prokaryotic signaling pathways for error checking and quality control enzyme group (5 enzymes): 2,918 amino acids
Total number of enzymes/proteins: 116 Total number of amino acids: 46,446–47,44617. Cellular Homeostasis and Signaling 1. Essential membrane proteins and channels group for cellular homeostasis (5 protein complexes): 2,180 amino acids
2. Protein phosphorylation code group (4 proteins): 1,294 amino acids
3. Protein dephosphorylation code group (4 proteins): 869 amino acids
4. Ion Transport Code group (4 proteins): 2,630 amino acids
5. DNA repair group (4 proteins): 1,430 amino acids
6. PI(4)P pathway (3 essential enzymes): 3,209 amino acids
7. Nutrient Sensing Code pathway (5 essential players): 6,468 amino acids
8. ATP/ADP Energy Balance Code pathway (5 essential players): 2,150 amino acids
9. Redox Code pathway (5 essential players): 2,640 amino acids
10. Osmoregulation Code pathway (5 essential players): 4,380 amino acids
11. Cytoskeleton Code pathway (5 essential players): 4,605 amino acids
12. Early pH Regulation Code pathway (5 essential players): 2,259 amino acids
13. Homeostasis Regulation Code pathway (5 essential players): 2,467 amino acids
14. Signaling pathways with bacterial lipids group (2 proteins): 550 amino acids
15. PhoR-PhoB system (3 key components): 890 amino acids
16. Signaling metabolite enzyme group (3 key enzymes): 1,050 amino acids
17. Quorum-sensing component group (2 key enzymes): 350 amino acids
18. LuxPQ-LuxU-LuxO system (3 key components): 1,410 amino acids
19. Quorum-sensing gene regulator group (3 key regulators): 720 amino acids
20. Transcriptional regulator group (3 key regulators): 600 amino acids
21. Essential post-translational modification enzyme group (3 key enzymes): 715 amino acids
Total number of enzymes/proteins: 95 Total number of amino acids: 47,87418. Stress Response and Defense Mechanisms 1. Ribosomal Rescue enzyme group (4 components): 1,761 amino acids and 363 nucleotides
2. Chaperone Proteins group (4 key chaperones): 2,767 amino acids
3. Maintain the Calcium Gradient enzyme group (4 enzymes): 1,522 amino acids
4. Basic Phosphate Homeostasis enzyme group (5 key components): 1,568 amino acids
5. Horizontal Gene Transfer (HGT) mechanisms enzyme group (4 enzymes): 1,526 amino acids
6. Stress response enzyme group (10 enzymes): 3,186 amino acids
7. Cellular defense enzyme group (3 enzymes): 1,398 amino acids
8. ROS management enzyme group (5 enzymes): 1,036 amino acids
9. Proteolysis pathway enzyme group (3 key enzymes): 1,215 amino acids
10. Proteolytic systems enzyme group (5 key enzymes): 1,788 amino acids
11. Lon protease (1 enzyme): 635 amino acids
12. Metalloprotease pathway enzyme group (3 key enzymes): 1,091 amino acids
13. Serine protease pathway enzyme group (3 key enzymes): 1,406 amino acids
14. Peptidase pathway enzyme group (3 key enzymes): 1,304 amino acids
15. Thermostable protein group (3 enzymes): 1,420 amino acids
Total number of enzymes/proteins: 60 Total number of amino acids: 23,62719. Biosynthesis and Metabolic Pathways 1. General secretion pathway components (11 key proteins/RNAs): 3,030 amino acids + 115 nucleotides
2. Acidocalcisome components and related enzymes (4 key proteins): 2,450 amino acids
3. Non-ribosomal peptide synthesis (1 key enzyme class): ~1,000 amino acids per module
4. Mevalonate pathway (6 key enzymes): 2,042 amino acids
5. Non-mevalonate pathway (7 key enzymes): 2,440 amino acids
6. Peptidoglycan biosynthesis pathway (7 key enzymes): 2,745 amino acids
7. Cross-linking process in peptidoglycan synthesis (2 key enzymes): 760 amino acids
Total number of enzymes/proteins: 38 Total number of amino acids: 14,467 + 115 nucleotides20. Metal Cluster and Cofactor Biosynthesis 1. Iron-Sulfur Cluster Proteins enzyme group (5 enzyme domains): 1,379 amino acids
2. Iron-sulfur cluster biosynthesis enzyme group (9 enzymes): 2,725 amino acids
3. [4Fe-4S] cluster synthesis pathway enzyme group (6 enzymes/proteins): 1,463 amino acids
4. Nickel center synthesis and incorporation group (6 proteins): 1,587 amino acids
5. [NiFe] cluster synthesis protein group (6 proteins): 1,850 amino acids
6. Iron-molybdenum cofactor ([Fe-Mo-Co]) synthesis protein group (6 proteins): 2,470 amino acids
7. [Fe-only] cluster synthesis protein group (6 proteins): 2,054 amino acids
8. [2Fe-2S]-[4Fe-4S] hybrid cluster synthesis protein group (6 proteins): 1,463 amino acids
9. Insertion and maturation of metal clusters into the CODH/ACS complex (10 proteins/enzymes): 3,405 amino acids
10. NRPS-related enzyme group for siderophore biosynthesis (4 key enzyme types): 2,768 amino acids
11. Siderophore export protein (1 protein): 400 amino acids
12. Ferrisiderophore transport and utilization process (4 key components): 1,250 amino acids
13. Sulfur mobilization process for Fe-S cluster biosynthesis (2 key enzymes): 792 amino acids
14. Sulfur transfer and Fe-S cluster assembly process (4 key enzymes): 1,180 amino acids
15. Scaffold Proteins for sulfur transfer
and Fe-S cluster assembly (7 key components): 2,250 amino acids
16. Heme biosynthesis pathway (8 key enzymes): 2,700 amino acids
17. Manganese utilization process (1 key enzyme): 200 amino acids
18. Mo/W cofactor biosynthesis pathway (4 key enzymes): 710 amino acids
19. Nickel center biosynthesis and incorporation pathway (4 key enzymes): 672 amino acids
20. Zinc utilization and management system (3 key proteins): 1,040 amino acids
21. Copper center utilization system (4 key enzymes): 1,208 amino acids
Total number of enzymes/proteins: 112 Total number of amino acids: 35,36621. Stress Response and Heat Shock Systems 1. Heat shock protein group (5 key components): 2,150 amino acids
2. Chaperone-assisted protein folding group (4 proteins): 1,912 amino acids
3. Protein disaggregation and repair system (3 enzymes): 1,307 amino acids
4. Hsp70-related folding machinery group (4 proteins): 2,450 amino acids
5. Cold shock response protein group (4 proteins): 1,211 amino acids
6. Heat shock regulatory system (4 proteins): 1,180 amino acids
7. Other stress-related repair systems (3 enzymes): 1,092 amino acids
8. ATP-dependent protease systems (5 proteins): 1,800 amino acids
9. Ubiquitin-like proteins in stress response (2 proteins): 607 amino acids
Total number of enzymes/proteins: 34 Total number of amino acids: 13,70922. Membrane and Lipid Homeostasis 1. Membrane integrity and lipid synthesis control group (4 key enzymes): 1,490 amino acids
2. Fatty acid transport systems (2 key transporters): 1,090 amino acids
3. Glycerolipid synthesis group (3 enzymes): 980 amino acids
4. Phosphatidic acid synthesis and control group (3 key proteins): 1,310 amino acids
5. CDP-diacylglycerol pathway enzymes (4 enzymes): 1,542 amino acids
6. Lipid degradation and recycling pathways (5 key enzymes): 2,010 amino acids
7. Specialized membrane lipid pathways (2 key components): 630 amino acids
Total number of enzymes/proteins: 23 Total number of amino acids: 9,05223. Detoxification and Waste Management Systems 1. Antioxidant enzyme systems (5 key enzymes): 1,410 amino acids
2. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) degradation enzyme group (5 enzymes): 1,305 amino acids
3. Nitrogen and sulfur detoxification pathways (3 enzymes): 1,150 amino acids
4. Glyoxylate and malate detoxification (2 key enzymes): 870 amino acids
5. Heavy metal detoxification systems (3 key proteins): 1,040 amino acids
6. Toxic byproduct elimination enzymes (4 enzymes): 1,505 amino acids
7. General waste product transporter group (3 proteins): 1,230 amino acids
Total number of enzymes/proteins: 25 Total number of amino acids: 8,51024. Cell Division and Growth Control 1. Cell division protein group (6 key components): 2,410 amino acids
2. Cell cycle regulatory protein group (5 proteins): 1,320 amino acids
3. FtsZ-related cytoskeletal components (4 proteins): 1,209 amino acids
4. Min system for bacterial division (3 proteins): 875 amino acids
5. Peptidoglycan synthesis and turnover (4 proteins): 1,200 amino acids
6. Septation and cytokinesis enzymes (5 proteins): 1,730 amino acids
7. Chromosome segregation proteins (3 proteins): 1,050 amino acids
Total number of enzymes/proteins: 30 Total number of amino acids: 9,79425. Miscellaneous Cellular Functions 1. General regulatory proteins (6 key regulators): 2,180 amino acids
2. Post-translational modification group (3 enzymes): 870 amino acids
3. Cellular motility system (4 key proteins): 2,205 amino acids
4. Endocytosis and vesicle trafficking systems (3 key enzymes): 1,255 amino acids
5. Signal transduction pathways (4 proteins): 1,790 amino acids
Total number of enzymes/proteins: 20 Total number of amino acids: 8,300Comprehensive Summary of the Minimal ProteomeTotal numbers across all sections are as follows:Total number of proteins/enzymes:
1,665 Total number of amino acids:
650,976 Total number of nucleotides:
6,185Ribonucleotides and Proteins in Prokaryotic SystemsThe molecular framework of prokaryotic systems is built on an interplay between ribonucleotides and proteins, which serve essential functions for cellular survival. These components form the backbone of translation machinery, essential for protein synthesis and overall cell function. The ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules are essential for decoding genetic instructions, while an array of proteins ensures that these processes occur efficiently. Prokaryotic cells utilize ribosomal RNAs as core structural and functional components of the ribosome, while transfer RNAs assist in translating genetic code into functional proteins. The process requires a sophisticated array of enzymes to charge tRNAs with amino acids, process tRNA molecules, and recycle them after use. This comprehensive set of components, including rRNA, tRNA, and associated proteins, forms a highly coordinated system critical for life. The remarkable efficiency and specificity of this molecular system challenge any notion that such a system could arise spontaneously, as each element must be finely tuned to interact with the others.In addition to rRNA and tRNA, a suite of initiation, elongation, and recycling factors orchestrates protein synthesis in a tightly regulated manner. These proteins, along with numerous enzymes involved in tRNA synthesis and aminoacylation, highlight the complexity required to maintain cellular function.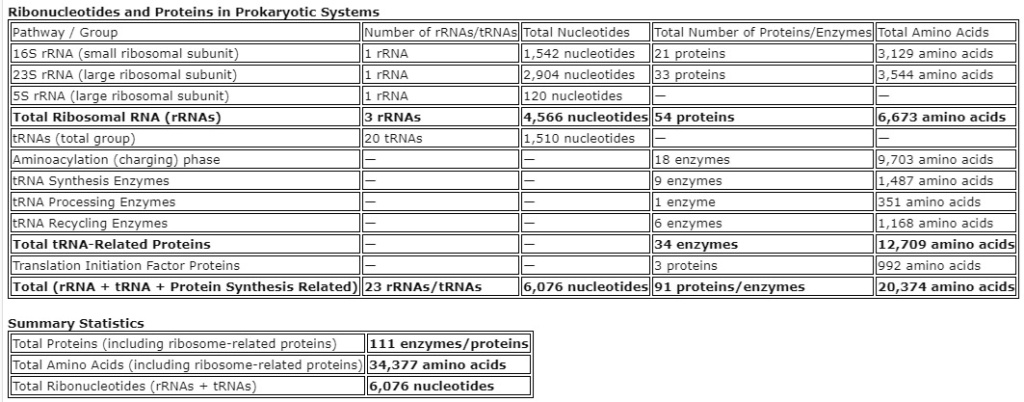 Ribonucleotides and Proteins in Prokaryotic Systems1. 16S rRNA (small ribosomal subunit): 1 rRNA, 1,542 nucleotides, 21 proteins (small subunit), 3,129 amino acids 2. 23S rRNA (large ribosomal subunit): 1 rRNA, 2,904 nucleotides, 33 proteins (large subunit), 3,544 amino acids 3. 5S rRNA (large ribosomal subunit): 1 rRNA, 120 nucleotides, — proteins, — amino acids 4. Total Ribosomal RNA (rRNAs): 3 rRNAs, 4,566 nucleotides, 54 proteins, 6,673 amino acids 5. tRNAs (total group): 20 tRNAs, 1,510 nucleotides, — proteins, — amino acids 6. Aminoacylation (charging) phase: — rRNAs, — nucleotides, 18 enzymes, 9,703 amino acids 7. tRNA Synthesis Enzymes: — rRNAs, — nucleotides, 9 enzymes, 1,487 amino acids 8. tRNA Processing Enzymes: — rRNAs, — nucleotides, 1 enzyme, 351 amino acids 9. tRNA Recycling Enzymes: — rRNAs, — nucleotides, 6 enzymes, 1,168 amino acids 10. Total tRNA-Related Proteins: — rRNAs, — nucleotides, 34 enzymes, 12,709 amino acids 11. Translation Initiation Factor Proteins: — rRNAs, — nucleotides, 3 proteins, 992 amino acids 12. Total (rRNA + tRNA + Protein Synthesis Related): 23 rRNAs/tRNAs, 6,076 nucleotides, 91 proteins, 20,374 amino acidsSummary Statistics
Ribonucleotides and Proteins in Prokaryotic Systems1. 16S rRNA (small ribosomal subunit): 1 rRNA, 1,542 nucleotides, 21 proteins (small subunit), 3,129 amino acids 2. 23S rRNA (large ribosomal subunit): 1 rRNA, 2,904 nucleotides, 33 proteins (large subunit), 3,544 amino acids 3. 5S rRNA (large ribosomal subunit): 1 rRNA, 120 nucleotides, — proteins, — amino acids 4. Total Ribosomal RNA (rRNAs): 3 rRNAs, 4,566 nucleotides, 54 proteins, 6,673 amino acids 5. tRNAs (total group): 20 tRNAs, 1,510 nucleotides, — proteins, — amino acids 6. Aminoacylation (charging) phase: — rRNAs, — nucleotides, 18 enzymes, 9,703 amino acids 7. tRNA Synthesis Enzymes: — rRNAs, — nucleotides, 9 enzymes, 1,487 amino acids 8. tRNA Processing Enzymes: — rRNAs, — nucleotides, 1 enzyme, 351 amino acids 9. tRNA Recycling Enzymes: — rRNAs, — nucleotides, 6 enzymes, 1,168 amino acids 10. Total tRNA-Related Proteins: — rRNAs, — nucleotides, 34 enzymes, 12,709 amino acids 11. Translation Initiation Factor Proteins: — rRNAs, — nucleotides, 3 proteins, 992 amino acids 12. Total (rRNA + tRNA + Protein Synthesis Related): 23 rRNAs/tRNAs, 6,076 nucleotides, 91 proteins, 20,374 amino acidsSummary Statistics- Total Proteins (including ribosome-related proteins):
91 enzymes/proteins
- Total Amino Acids (including ribosome-related proteins):
20,374 amino acids
- Total Ribonucleotides (rRNAs + tRNAs):
6,076 nucleotides
Alignment of List with Summary1.
Total Proteins (including ribosome-related proteins) - 91 proteins are directly mentioned in the detailed list under "Total (rRNA + tRNA + Protein Synthesis Related)".
2.
Total Amino Acids (including ribosome-related proteins) - The total amino acids in the list sum up to 20,374 amino acids (from the detailed list of proteins), which matches the summary.
3.
Total Ribonucleotides (rRNAs + tRNAs) - The total number of nucleotides from the rRNAs is 4,566 nucleotides, and from the tRNAs it is 1,510 nucleotides, giving a total of 6,076 nucleotides, which also aligns with the summary.



