photosynthesis is a interdependent system. Unless following enzymes and protein complexes are present, photosynthesis will not occur
In photosynthesis , 26 protein complexes and enzymes are required to go through the light and light independent reactions, using light energy to get glucose as end product , a metabolic intermediate for cell respiration. The protein complexes are uniquely used in photosynthesis. The pathway must go all the way through, and all steps are required, otherwise glucose is not produced. Also, in the oxygen evolving complex, which splits water into electrons, protons, and CO2, if the light-induced electron transfer reactions do not go all the five steps through, no oxygen, no protons and electrons are produced, no advanced life would be possible on earth. So, photosynthesis is a interdependent system, that could not have evolved, since all parts had to be in place right from the beginning. So it seems that photosynthesis falsifies the theory of evolution, where all small steps need to provide a survival advantage.
Light-dependent reactions
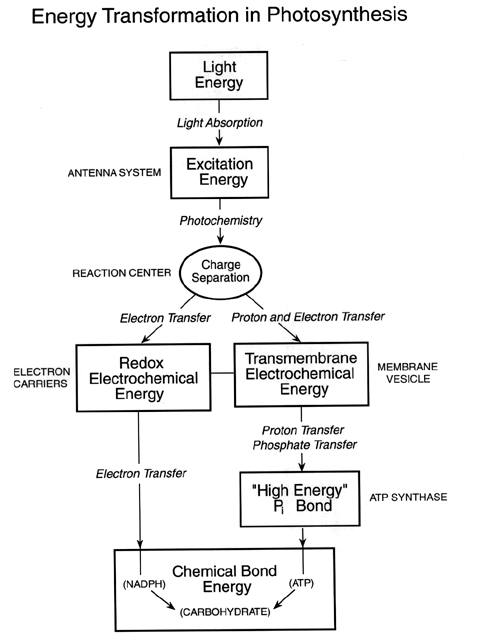
The light-dependent reactions, or photoreduction, is the first stage of photosynthesis, is a process by which plants capture and store energy from sunlight. In this process, light energy is converted into chemical energy, in the form of the energy-carrying molecules ATP and NADPH. In the light-independent reactions, the formed NADPH and ATP drive the reduction of CO2 to more useful organic compounds, such as glucose.
For the light reactions following enzymes and proteins complexes are needed
Thylakoid membrane
Chlorophyll pigments
Light harvesting complex
Photosystem II
Photosystem II reaction Center
Oxygen evolving complex
other accessory pigments
Pheophytin
Plastoquinone
Cytochrome b6f complex
Plastocyanin
Photosystem I
Photosystem I reaction Center
Iron-sulfur protein
Ferredoxin
ATP synthase enzyme

Light-independent reactions
The Calvin cycle describes the synthesis of glucose from carbon dioxide and water by oxygen-producing photosynthesis. It uses sunlight for energy.
The second step, called the Calvin cycle, the actual fixation of carbon dioxide is carried out. This process consumes ATP and NADPH. The Calvin cycle in plants accounts for the preponderance of carbon fixation on land. In algae and cyanobacteria, it accounts for the preponderance of carbon fixation in the oceans.
Rubisco
Phosphoglycerate kinase
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (NADP+) (phosphorylating)
Triosephosphate isomerase
Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase
Transketolase
Aldolase
Sedoheptulose-bisphosphatase
Transketolase
Ribose-5-phosphate isomerase
Phosphoribulokinase


In photosynthesis , 26 protein complexes and enzymes are required to go through the light and light independent reactions, using light energy to get glucose as end product , a metabolic intermediate for cell respiration. The protein complexes are uniquely used in photosynthesis. The pathway must go all the way through, and all steps are required, otherwise glucose is not produced. Also, in the oxygen evolving complex, which splits water into electrons, protons, and CO2, if the light-induced electron transfer reactions do not go all the five steps through, no oxygen, no protons and electrons are produced, no advanced life would be possible on earth. So, photosynthesis is a interdependent system, that could not have evolved, since all parts had to be in place right from the beginning. So it seems that photosynthesis falsifies the theory of evolution, where all small steps need to provide a survival advantage.
Light-dependent reactions
The light-dependent reactions, or photoreduction, is the first stage of photosynthesis, is a process by which plants capture and store energy from sunlight. In this process, light energy is converted into chemical energy, in the form of the energy-carrying molecules ATP and NADPH. In the light-independent reactions, the formed NADPH and ATP drive the reduction of CO2 to more useful organic compounds, such as glucose.
For the light reactions following enzymes and proteins complexes are needed
Thylakoid membrane
Chlorophyll pigments
Light harvesting complex
Photosystem II
Photosystem II reaction Center
Oxygen evolving complex
other accessory pigments
Pheophytin
Plastoquinone
Cytochrome b6f complex
Plastocyanin
Photosystem I
Photosystem I reaction Center
Iron-sulfur protein
Ferredoxin
ATP synthase enzyme


Light-independent reactions
The Calvin cycle describes the synthesis of glucose from carbon dioxide and water by oxygen-producing photosynthesis. It uses sunlight for energy.
The second step, called the Calvin cycle, the actual fixation of carbon dioxide is carried out. This process consumes ATP and NADPH. The Calvin cycle in plants accounts for the preponderance of carbon fixation on land. In algae and cyanobacteria, it accounts for the preponderance of carbon fixation in the oceans.
Rubisco
Phosphoglycerate kinase
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (NADP+) (phosphorylating)
Triosephosphate isomerase
Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase
Transketolase
Aldolase
Sedoheptulose-bisphosphatase
Transketolase
Ribose-5-phosphate isomerase
Phosphoribulokinase

Last edited by Admin on Thu May 05, 2016 1:01 pm; edited 18 times in total

