What are the REAL mechanisms of biodiversity, replacing macroevolution?
Where Do Complex Organisms Come From?
What are the REAL mechanisms of biodiversity, replacing macroevolution?
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Sm5dcr4Shpo&feature=youtu.be
https://reasonandscience.catsboard.com/t2316-evolution-where-do-complex-organisms-come-from
Based on evidence seen in biochemistry on a molecular level, we can now say affirmatively and conclusively, that Darwins theory of evolution by natural selection in regards of first degree speciation & macroevolutionary level has been falsified.
The real mechanisms that explain biodiversity and complex organismal architecture is preprogrammed instructional complex INFORMATION encoded in various genetic and epigenetic languages and communication by various signalling codes through various signalling networks
That brings us to the origin by an intelligent designer.
Pinpointing what REALLY defines body architecture, the orchestration of organism development, cell shape and body form and the mechanisms of adaptation and primary speciation, and exposing the correct explanation of biochemical mechanisms of biodiversity is the holy grail of biological sciences. Preprogrammed codified information and signalling replaces Darwin's theory and its various subsequent adaptations, extensions, and new proposals like the modern extended synthesis or the so-called " third way ". The true mechanism is " Biochemical systems programming and signalling", and special creation of species and/or kinds by an intelligent powerful creator. Long periods of time and gradual, evolutionary development is not possible, face the fact that cells and organisms work like gigantic interlocked machines and factory complexes, where in any case, if one tiny part is missing, nothing goes. Natural selection would not select for components of a complex system that would be useful only in the completion of that much larger system. No glycine amino acids, no pyrimidines, no DNA - no life. No Watson Crick base pair fine-tuning, no DNA - no life. No ribosomal mechanism for amino acid amide bondage, no proteins, no life. No nitrogenase enzymes to fix nitrogen in an energy demanding, triple bond breaking process, no ammonia, required to make amino acids - no nitrogen cycle - no advanced life. No chlorophylls, no absorption of light to start photosynthesis, no starch and glucose - cells will have no food supply to sustain complex organisms - no advanced life on earth. No rubisco, no fix of CO2, no hydrocarbons - no advanced life. No counterion in retinal, and rhodopsin could not receive visible light - and there would be no vision on earth by any organism.
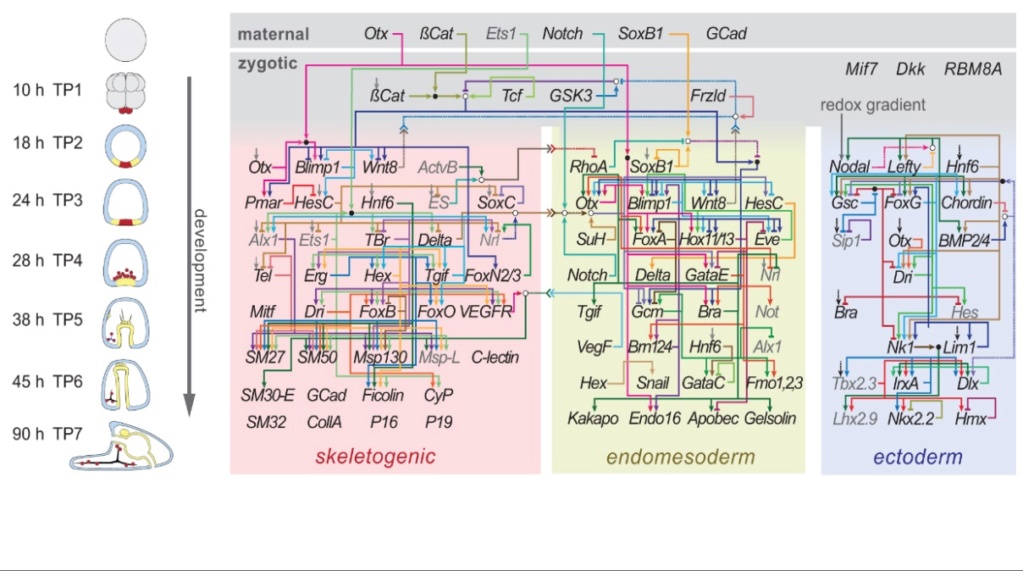
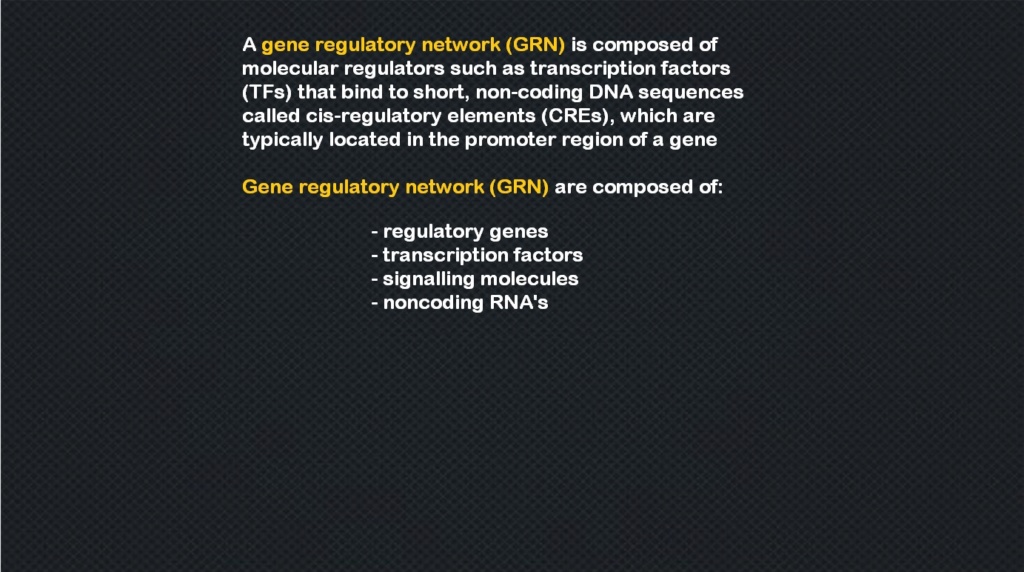
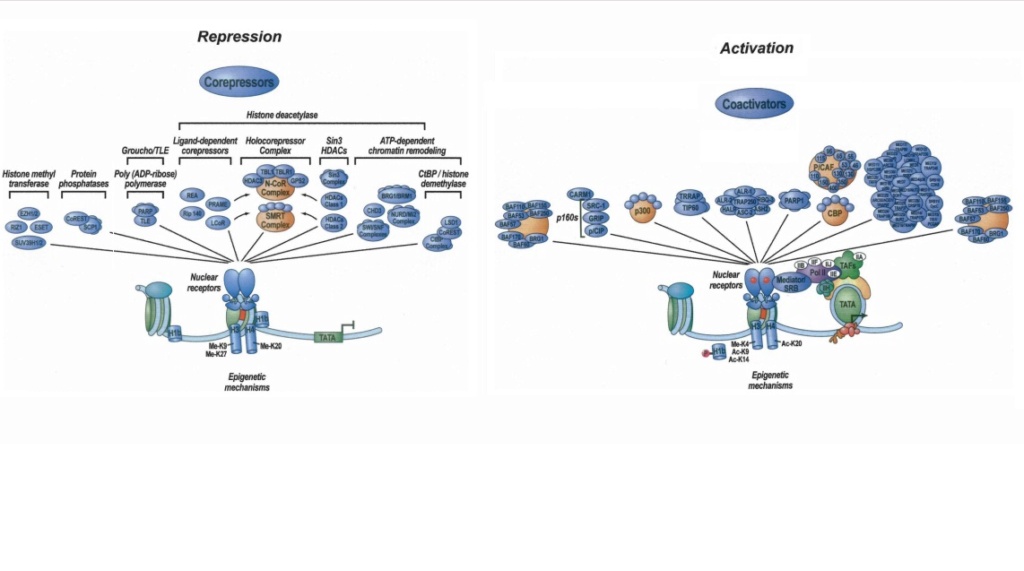
1. The Gene regulation network orchestrates gene expression
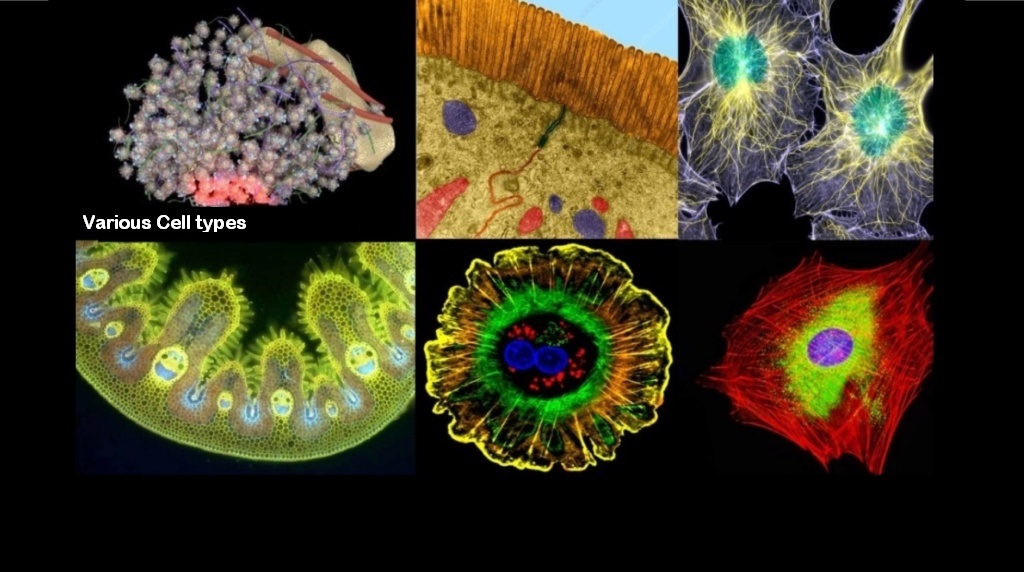
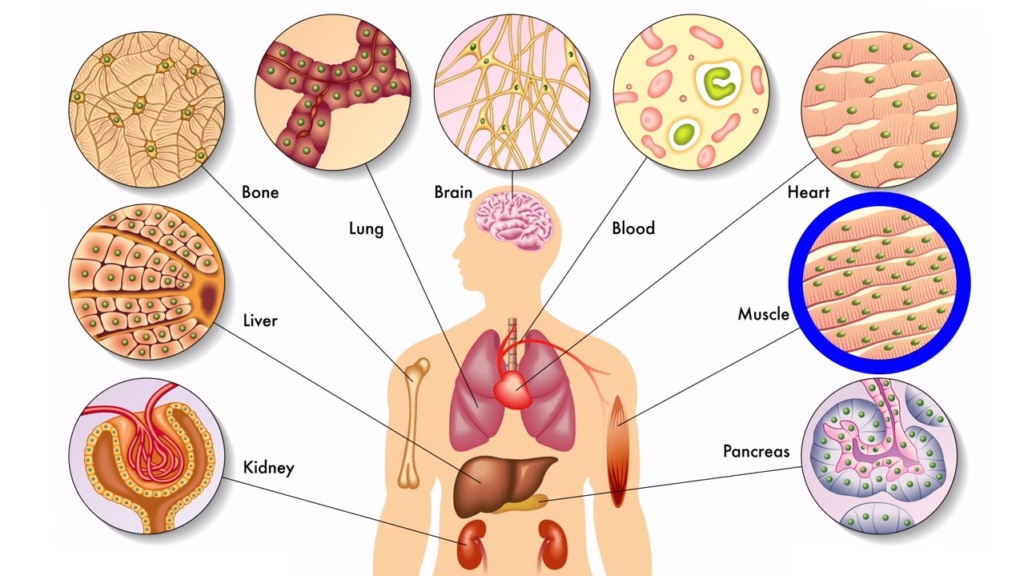
2. Various signalling pathways generate Cell types and patterns
3. At least 23 Epigenetic Codes are multidimensional and perform various tasks essential to cell structure and development
4. Cell-Cell communication in various forms, especially important for animal development
5. Chromatin dance in the nucleus through extensile motors affect transcription and gene regulation
6. Post-transcriptional modifications (PTMs) of histones affect gene transcription
7. The DNA methylation code is like a barcode or marker, the methyl group indicates, for instance, which genes in the DNA are to be turned on.
8. Homeobox and Hox genes determine the shape of the body.
9. Noncoding DNA ( Junk DNA ) is transcribed into functional non-coding RNA molecules and switches protein-coding genes on or off.
10. Transposons and Retrotransposons regulate genes
11. Centrosomes play a central role in development
12. The precise arrangement of Cytoskeletal arrays provides critical structural information.
13. Membrane targets provide crucial information—spatial coordinates—for embryological development.
14. Ion Channels and Electromagnetic Fields influence the form of a developing organism
15. The Sugar Code forms information-rich structures which influence the arrangement of different cell types during embryological development.
16. Egg-polarity genes encode macromolecules deposited in the egg to organize the axes
17. Hormones are special chemical messengers for development

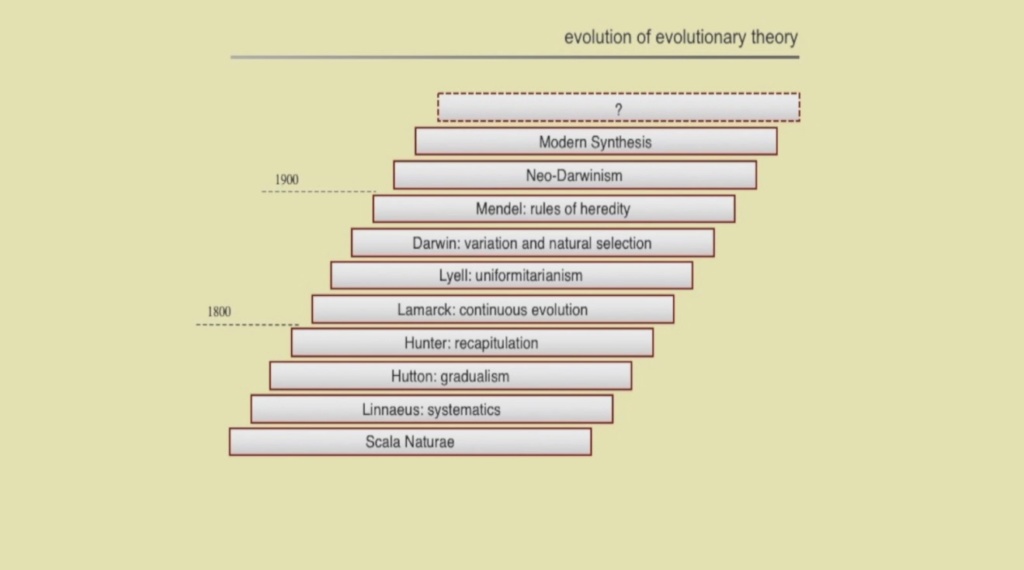
The question of where life, biodiversity and organismal complexity came from has always been one of the fundamental, existential questions of humanity, and is today covered in modern science by evolutionary biology.

The question if Darwin's theory is a fact, is as well a core question in the evolution - creation debate. Some atheists regard evolution as one of the main reasons to discard creationism, and as consequence theism is viewed with skepticism and incredulity.

In 1859, Darwin published " On the origin of species", which has become the foundation of modern biological sciences until today.
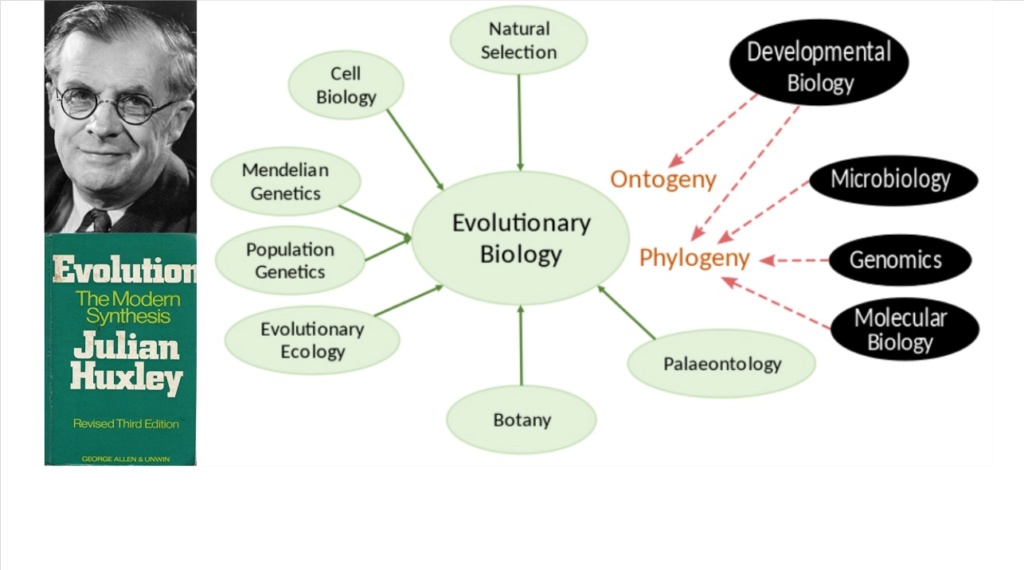
In 1942 Julian Huxley, a British evolutionary biologist, published the book, Evolution: The Modern Synthesis. which was a fusion of various disciplines like genetics, covered by population genetics, experimental
genetics and systematics, palaeontology, botany and so on.
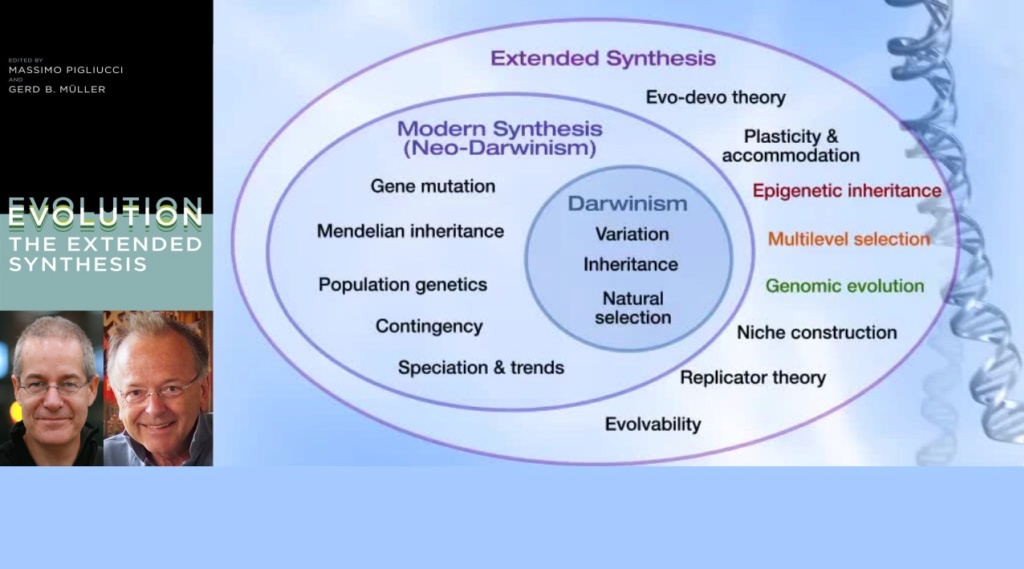
The modern synthesis went gradually through further improvements, and a more recent version was a new conceptual framework proposed in 2007 by Massimo Pigliucci and Gerd B. Müller in their book: Extended evolutionary synthesis.
They incorporated new information from molecular genetics and genomics, describing new kinds of hereditary and replicatory mechanisms which were not considered within the framework of the previous versions.

Many books have been written over the years, with the purpose to disprove Darwin's theory, and many, pointing out successfully, why his theory does not withstand scrutiny.

The number of scientists of various biological disciplines and biochemistry who disagree has grown into the thousands.

One group declared: We are skeptical of claims for the ability of random mutation and natural selection to account for the complexity of life.

The claim of the standard theory is that a rather small toolkit of genetic modifications during long periods of time, based on random genetic errors, explains the rise of genetic modification, and new information, and as a result, the enormous range of biodiversity, proposing mutations and natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, and artificial breeding by human intervention as why descends are modified.

In 2017, Gerd B. Müller, theoretical biologist stated: Biological sciences have made significant advances in the last decades, providing a wealth of new knowledge about the factors responsible for organismal development processes. The modern synthesis and its various additions concentrate on genetic and adaptive variation in populations.
An extended framework emphasizes the role of epigenetic processes, ecological interactions and systems dynamics in the make of organismal complexity.
Single-level and unilinear causation is replaced by multilevel and reciprocal causation. Among other consequences, the extended framework overcomes many of the limitations of traditional gene-centric explanations.

several of the cornerstones of the traditional evolutionary framework need to be revised and new components incorporated into a common theoretical structure.
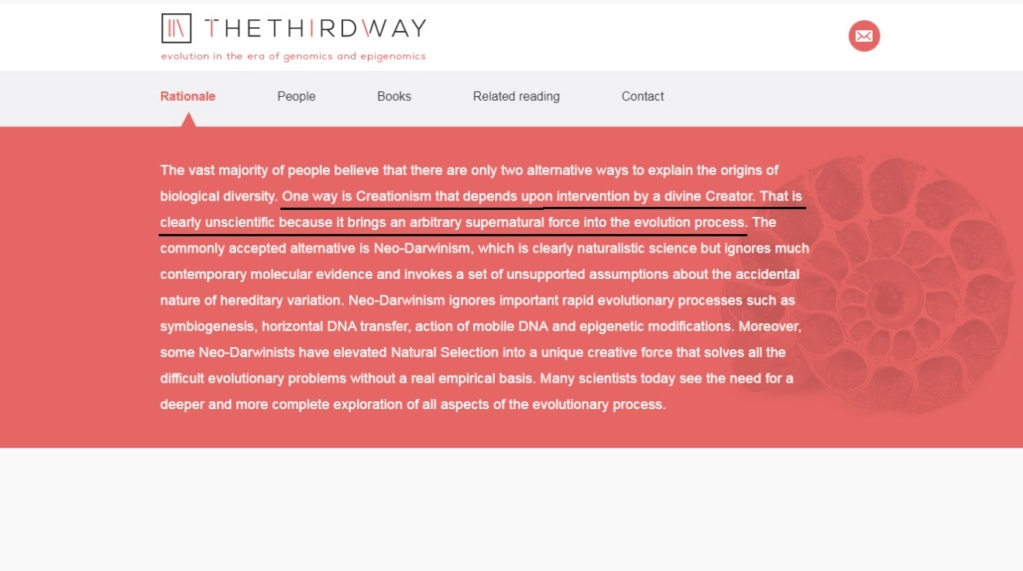
Gerd B. Müller is part of a group of scientists which propose an alternative to the standard evolutionary model, called The third way. Remarkably, in their opening statement, they say that Creationism depends upon intervention by a divine Creator. That is clearly unscientific because it brings an arbitrary supernatural force into the evolution process.
First of all, it has not been established beyond any doubt, that naturalistic evolutionary processes account for biodiversity. Scientific investigation should permit the evidence to lead wherever it is, without excluding intelligent causation a priori.
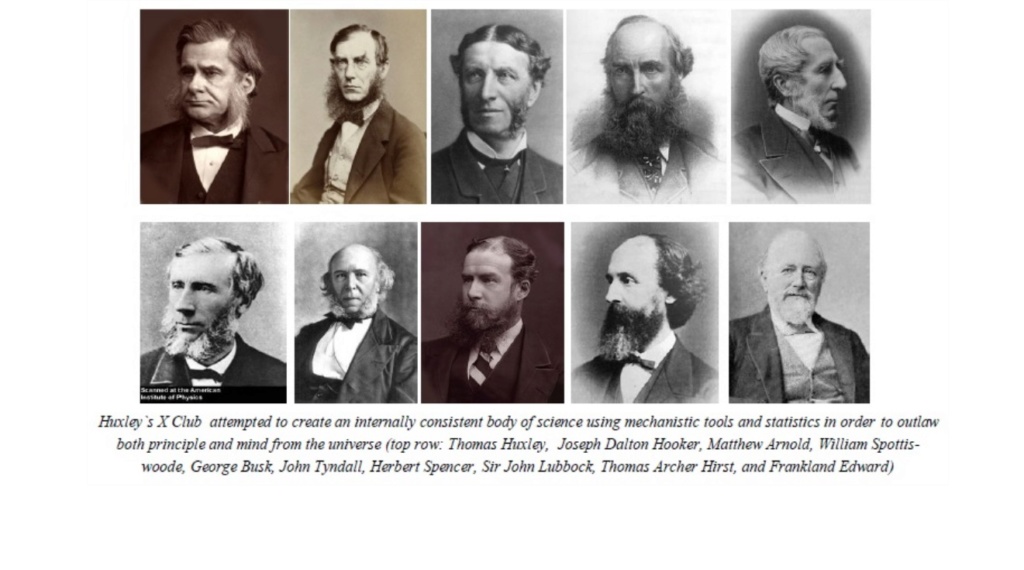

Excluding one possible answer, namely, intelligent design means committing the same philosophical error as back in the nineteenth century, with the X-Club, and Darwins Bulldog, Thomas Huxley, when they did the same.
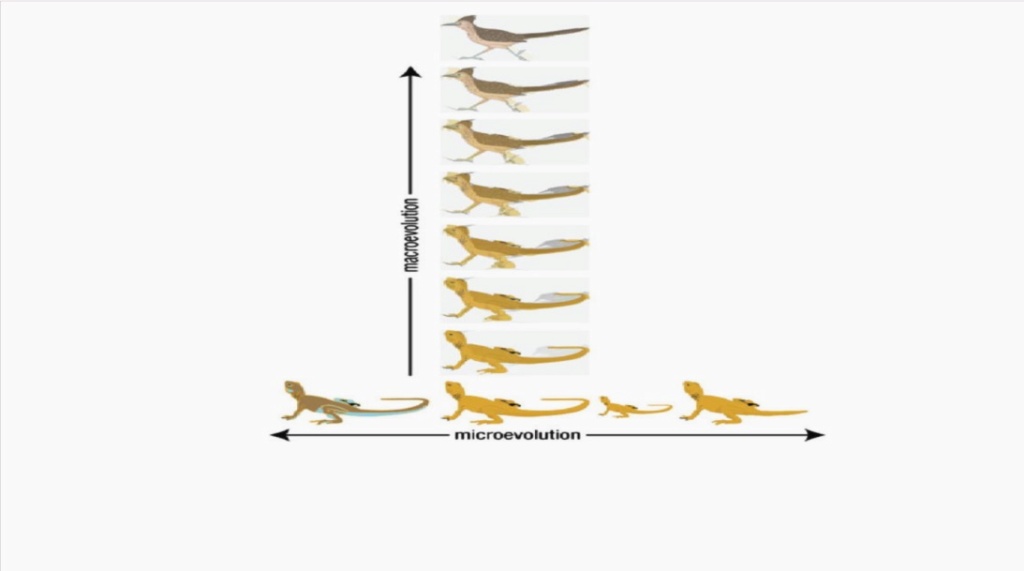
An important distinction is made between micro and macroevolution. The common claim is that small changes lead over a time period of billions of years, to big changes, and small variations permit the arising of new biological structures and functions, and levels of complexity.
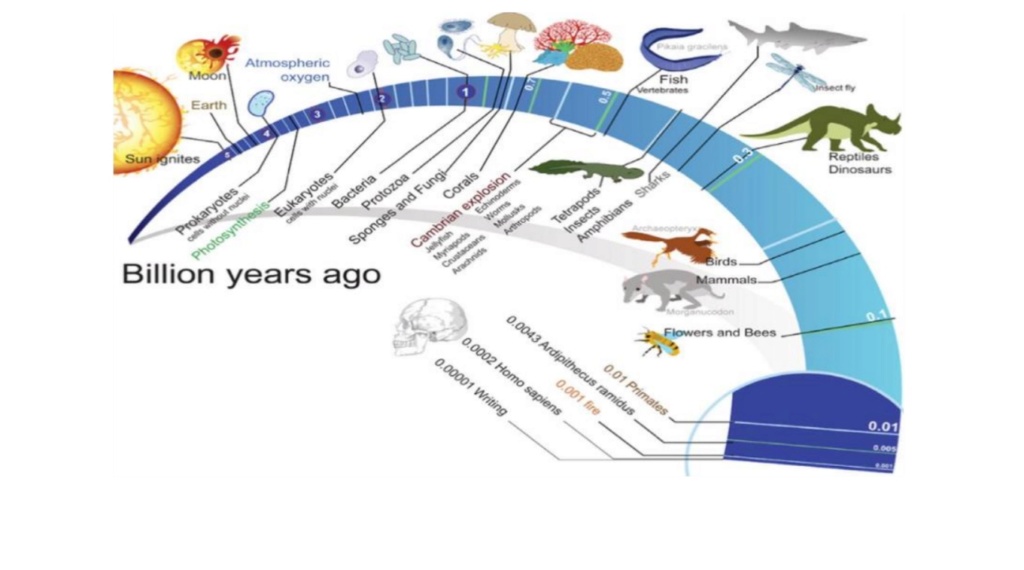
From a universal common ancestor to all forms of life. This claim, however, has never been shown to be true.

It is a common assertion, even held today by the majority of biologists, that microevolution leads to macroevolution. The article in Nature magazine, for example, claims in its conclusion remarks:
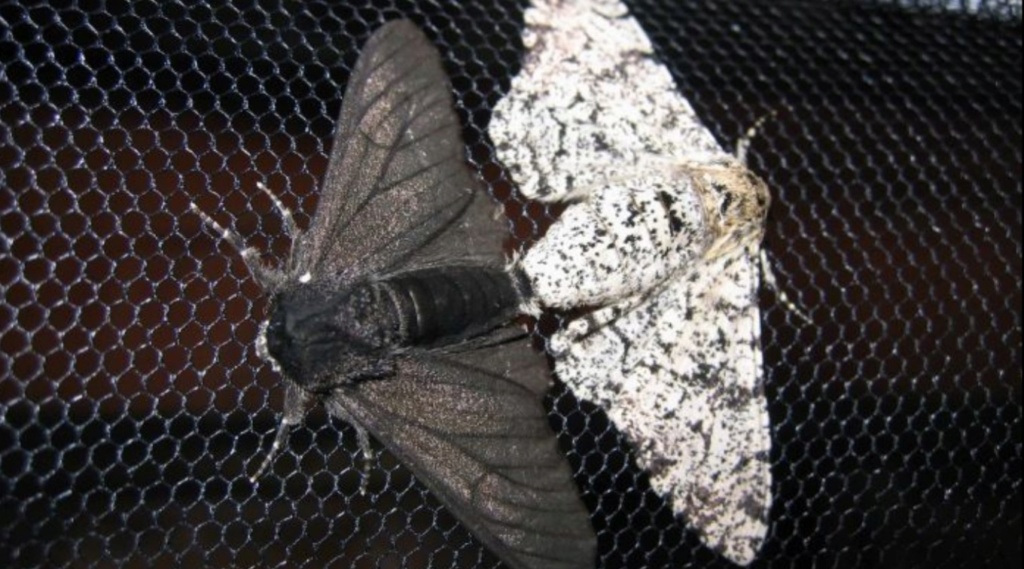


Let's clarify: Organisms can and do adapt to their environment, which is often described as microevolution, but would be better described as adaptation. It is life essential and had to be fully set up when life began. Natural selection on a limited scale is a fact, but even in regards to adaptation or microevolution, not the main driving mechanism that explains it.

The main dispute is the claim that all organisms descent from a universal common ancestor, and the idea that unguided, unintelligent natural processes explain biodiversity. In his book, Darwin suggests that all living organisms are related by ascendency, and therefore they are all derived from ancestral species, which migrate around the world and diversify, generating the amazing biodiversity of organisms.
Variational plasticity and adaptation which are mentioned in points 1 to 5 are empirically demonstrated facts. What is in dispute, however, are point 6 and 7. Universal Common Ancestry, and macroevolution. The claim that all biodiversity is explained by unguided, unintelligent, purposeless natural processes, without intelligence involved.
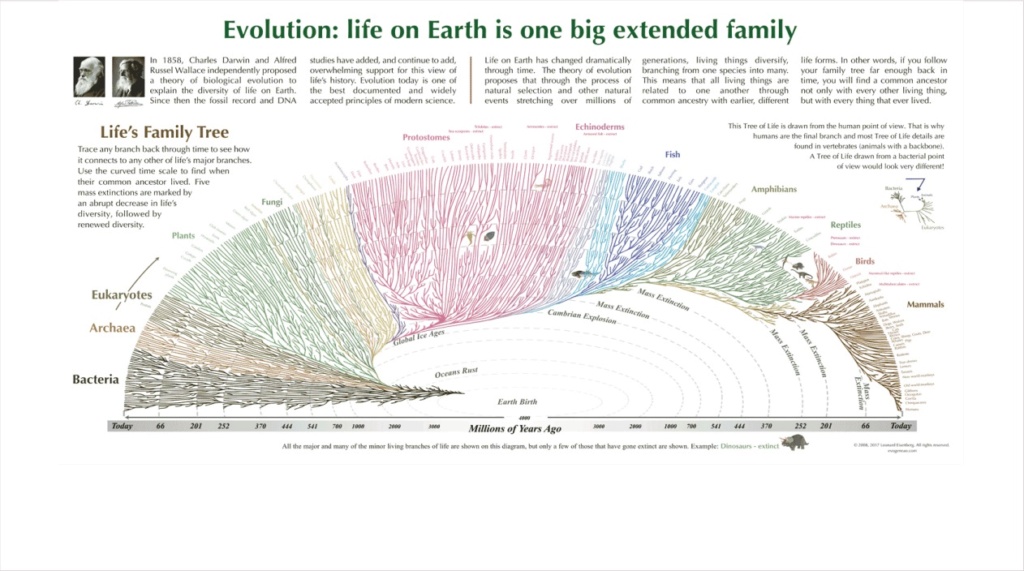
There are various aspects and ways of how we can analyze evolution. Like for example doing comparative anatomy, systematic classification of life and the elaboration of the supposed phylogenetic tree of life,
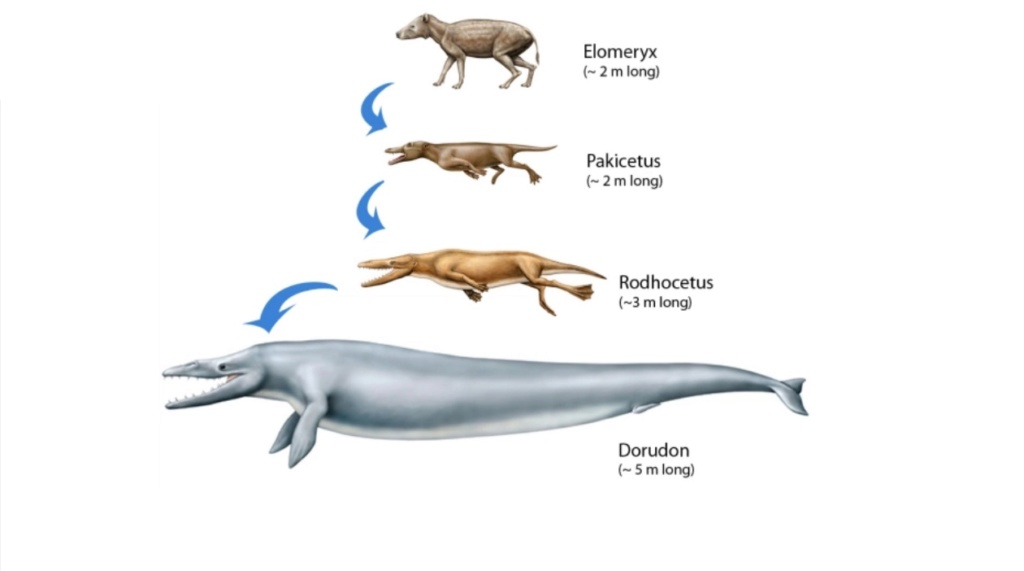
then there is the analysis of the fossil record by paleontologists, and the attempt to establish a line of transitional fossils demonstrating evolution,
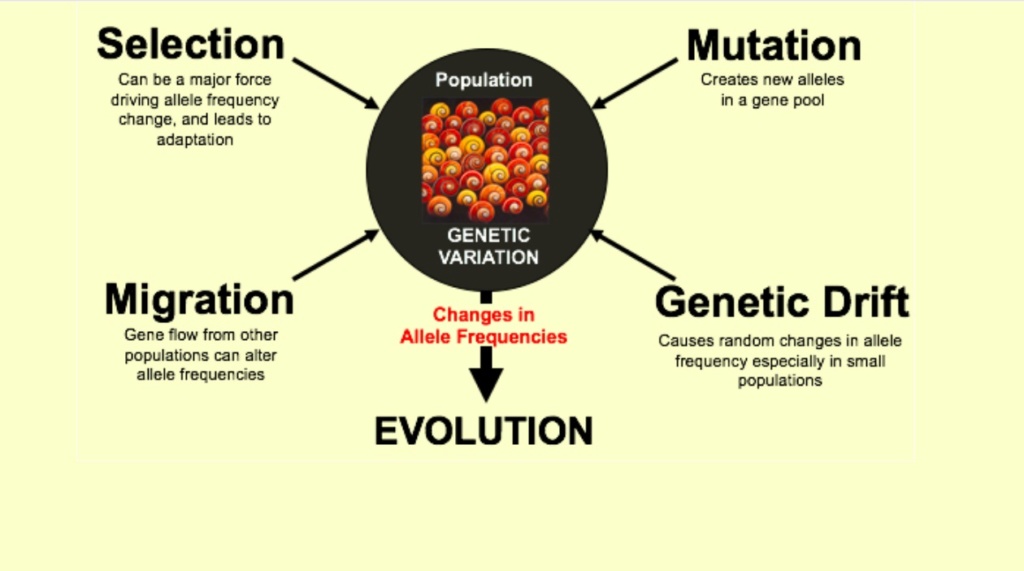
variation in population genetics, quantitative genetics, how it is modified under certain selectional regimes
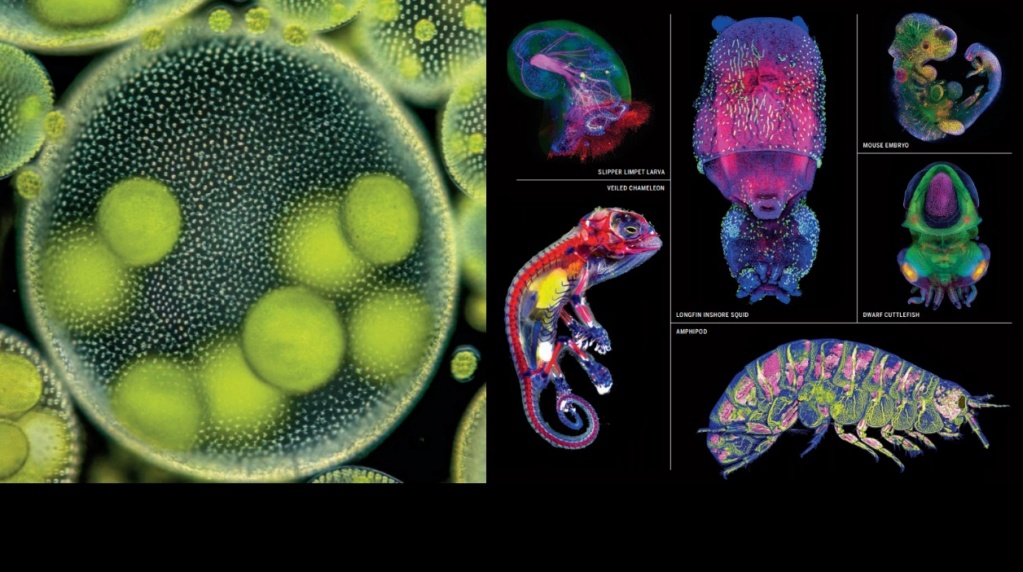
and another aspect is the investigation of how organisms acquire more and more complexity, the emergence of varied body plans, architectures, physiology and functions,
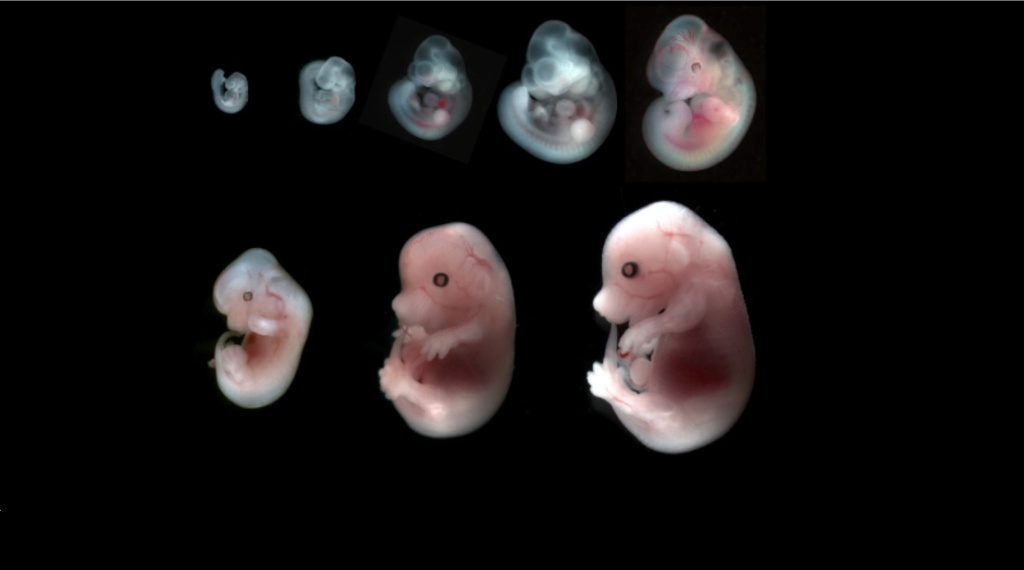
and there is the aspect and question of evo-devo, of development biology, that compares the developmental processes of different organisms to infer the ancestral relationships between them and how developmental processes supposedly evolved.

and last not least, the origin of consciousness, mind, logic, speech, languages, covered by anthropology, linguistics, social sciences etc.

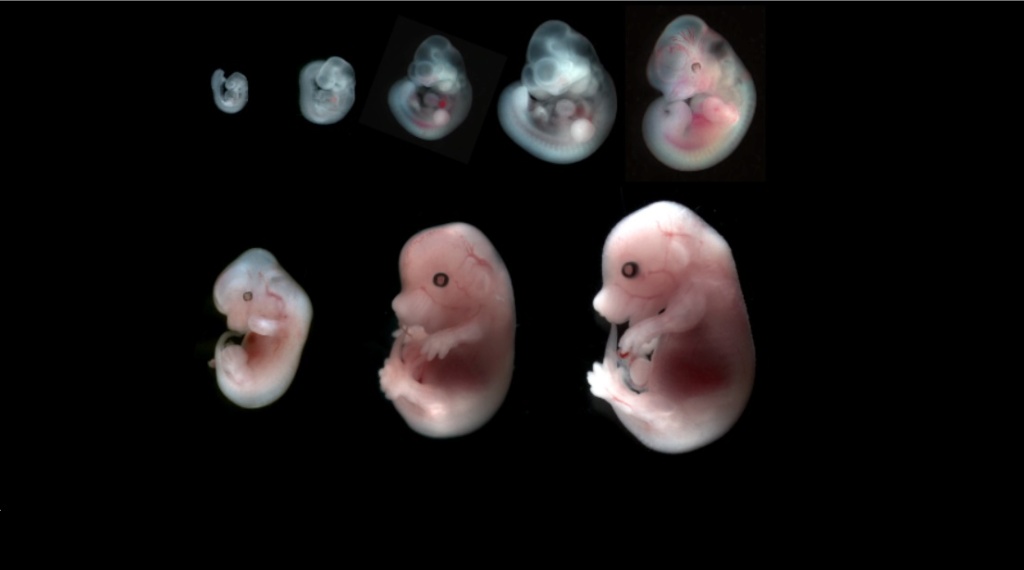
Before we can ask about the mechanisms and the origin and maintenance of body plans, we need to ask what is currently responsible for the development of complex multicellularity, and organismal architecture, form, and cell shape.
We need to understand how an organism develops to adulthood, which permits us with that framework as a starting point to do top-down research to understand how the responsible tool kit and rules for organismal complexity could have emerged in the past.
In fact, it is a development program, which sets how a multicellular organism develops. So we have to define what that development program consists of, in order to know what has to change, for an organism to change its physiology and complexity.

So that change of the development program is what would have to change for an organism to change, and that has given rise to very varied programs of evolutionary disciplines and research programs.
It has become more and more evidently clear, that a varied multitude of different mechanisms is responsible for body constructions, which are not limited to genetics, but mainly, if not even more important, epigenetic factors,
and not only on an intracellular level, but physiology on a multilayered level, which is investigated in systems biology.

The real mechanisms that explain biodiversity and complex organismal architecture is preprogrammed instructional complex INFORMATION encoded in various genetic and epigenetic languages and communication by various signalling codes through various signalling networks.

That brings us to the origin of all life forms by an intelligent designer.
Where Do Complex Organisms Come From?
What are the REAL mechanisms of biodiversity, replacing macroevolution?
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Sm5dcr4Shpo&feature=youtu.be
https://reasonandscience.catsboard.com/t2316-evolution-where-do-complex-organisms-come-from
Based on evidence seen in biochemistry on a molecular level, we can now say affirmatively and conclusively, that Darwins theory of evolution by natural selection in regards of first degree speciation & macroevolutionary level has been falsified.
The real mechanisms that explain biodiversity and complex organismal architecture is preprogrammed instructional complex INFORMATION encoded in various genetic and epigenetic languages and communication by various signalling codes through various signalling networks
That brings us to the origin by an intelligent designer.
Pinpointing what REALLY defines body architecture, the orchestration of organism development, cell shape and body form and the mechanisms of adaptation and primary speciation, and exposing the correct explanation of biochemical mechanisms of biodiversity is the holy grail of biological sciences. Preprogrammed codified information and signalling replaces Darwin's theory and its various subsequent adaptations, extensions, and new proposals like the modern extended synthesis or the so-called " third way ". The true mechanism is " Biochemical systems programming and signalling", and special creation of species and/or kinds by an intelligent powerful creator. Long periods of time and gradual, evolutionary development is not possible, face the fact that cells and organisms work like gigantic interlocked machines and factory complexes, where in any case, if one tiny part is missing, nothing goes. Natural selection would not select for components of a complex system that would be useful only in the completion of that much larger system. No glycine amino acids, no pyrimidines, no DNA - no life. No Watson Crick base pair fine-tuning, no DNA - no life. No ribosomal mechanism for amino acid amide bondage, no proteins, no life. No nitrogenase enzymes to fix nitrogen in an energy demanding, triple bond breaking process, no ammonia, required to make amino acids - no nitrogen cycle - no advanced life. No chlorophylls, no absorption of light to start photosynthesis, no starch and glucose - cells will have no food supply to sustain complex organisms - no advanced life on earth. No rubisco, no fix of CO2, no hydrocarbons - no advanced life. No counterion in retinal, and rhodopsin could not receive visible light - and there would be no vision on earth by any organism.
1. The Gene regulation network orchestrates gene expression
2. Various signalling pathways generate Cell types and patterns
3. At least 23 Epigenetic Codes are multidimensional and perform various tasks essential to cell structure and development
4. Cell-Cell communication in various forms, especially important for animal development
5. Chromatin dance in the nucleus through extensile motors affect transcription and gene regulation
6. Post-transcriptional modifications (PTMs) of histones affect gene transcription
7. The DNA methylation code is like a barcode or marker, the methyl group indicates, for instance, which genes in the DNA are to be turned on.
8. Homeobox and Hox genes determine the shape of the body.
9. Noncoding DNA ( Junk DNA ) is transcribed into functional non-coding RNA molecules and switches protein-coding genes on or off.
10. Transposons and Retrotransposons regulate genes
11. Centrosomes play a central role in development
12. The precise arrangement of Cytoskeletal arrays provides critical structural information.
13. Membrane targets provide crucial information—spatial coordinates—for embryological development.
14. Ion Channels and Electromagnetic Fields influence the form of a developing organism
15. The Sugar Code forms information-rich structures which influence the arrangement of different cell types during embryological development.
16. Egg-polarity genes encode macromolecules deposited in the egg to organize the axes
17. Hormones are special chemical messengers for development


The question of where life, biodiversity and organismal complexity came from has always been one of the fundamental, existential questions of humanity, and is today covered in modern science by evolutionary biology.

The question if Darwin's theory is a fact, is as well a core question in the evolution - creation debate. Some atheists regard evolution as one of the main reasons to discard creationism, and as consequence theism is viewed with skepticism and incredulity.

In 1859, Darwin published " On the origin of species", which has become the foundation of modern biological sciences until today.

In 1942 Julian Huxley, a British evolutionary biologist, published the book, Evolution: The Modern Synthesis. which was a fusion of various disciplines like genetics, covered by population genetics, experimental
genetics and systematics, palaeontology, botany and so on.

The modern synthesis went gradually through further improvements, and a more recent version was a new conceptual framework proposed in 2007 by Massimo Pigliucci and Gerd B. Müller in their book: Extended evolutionary synthesis.
They incorporated new information from molecular genetics and genomics, describing new kinds of hereditary and replicatory mechanisms which were not considered within the framework of the previous versions.

Many books have been written over the years, with the purpose to disprove Darwin's theory, and many, pointing out successfully, why his theory does not withstand scrutiny.

The number of scientists of various biological disciplines and biochemistry who disagree has grown into the thousands.

One group declared: We are skeptical of claims for the ability of random mutation and natural selection to account for the complexity of life.

The claim of the standard theory is that a rather small toolkit of genetic modifications during long periods of time, based on random genetic errors, explains the rise of genetic modification, and new information, and as a result, the enormous range of biodiversity, proposing mutations and natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, and artificial breeding by human intervention as why descends are modified.

In 2017, Gerd B. Müller, theoretical biologist stated: Biological sciences have made significant advances in the last decades, providing a wealth of new knowledge about the factors responsible for organismal development processes. The modern synthesis and its various additions concentrate on genetic and adaptive variation in populations.
An extended framework emphasizes the role of epigenetic processes, ecological interactions and systems dynamics in the make of organismal complexity.
Single-level and unilinear causation is replaced by multilevel and reciprocal causation. Among other consequences, the extended framework overcomes many of the limitations of traditional gene-centric explanations.

several of the cornerstones of the traditional evolutionary framework need to be revised and new components incorporated into a common theoretical structure.

Gerd B. Müller is part of a group of scientists which propose an alternative to the standard evolutionary model, called The third way. Remarkably, in their opening statement, they say that Creationism depends upon intervention by a divine Creator. That is clearly unscientific because it brings an arbitrary supernatural force into the evolution process.
First of all, it has not been established beyond any doubt, that naturalistic evolutionary processes account for biodiversity. Scientific investigation should permit the evidence to lead wherever it is, without excluding intelligent causation a priori.

Excluding one possible answer, namely, intelligent design means committing the same philosophical error as back in the nineteenth century, with the X-Club, and Darwins Bulldog, Thomas Huxley, when they did the same.

An important distinction is made between micro and macroevolution. The common claim is that small changes lead over a time period of billions of years, to big changes, and small variations permit the arising of new biological structures and functions, and levels of complexity.

From a universal common ancestor to all forms of life. This claim, however, has never been shown to be true.

It is a common assertion, even held today by the majority of biologists, that microevolution leads to macroevolution. The article in Nature magazine, for example, claims in its conclusion remarks:


Let's clarify: Organisms can and do adapt to their environment, which is often described as microevolution, but would be better described as adaptation. It is life essential and had to be fully set up when life began. Natural selection on a limited scale is a fact, but even in regards to adaptation or microevolution, not the main driving mechanism that explains it.

The main dispute is the claim that all organisms descent from a universal common ancestor, and the idea that unguided, unintelligent natural processes explain biodiversity. In his book, Darwin suggests that all living organisms are related by ascendency, and therefore they are all derived from ancestral species, which migrate around the world and diversify, generating the amazing biodiversity of organisms.
Variational plasticity and adaptation which are mentioned in points 1 to 5 are empirically demonstrated facts. What is in dispute, however, are point 6 and 7. Universal Common Ancestry, and macroevolution. The claim that all biodiversity is explained by unguided, unintelligent, purposeless natural processes, without intelligence involved.

There are various aspects and ways of how we can analyze evolution. Like for example doing comparative anatomy, systematic classification of life and the elaboration of the supposed phylogenetic tree of life,

then there is the analysis of the fossil record by paleontologists, and the attempt to establish a line of transitional fossils demonstrating evolution,

variation in population genetics, quantitative genetics, how it is modified under certain selectional regimes

and another aspect is the investigation of how organisms acquire more and more complexity, the emergence of varied body plans, architectures, physiology and functions,

and there is the aspect and question of evo-devo, of development biology, that compares the developmental processes of different organisms to infer the ancestral relationships between them and how developmental processes supposedly evolved.

and last not least, the origin of consciousness, mind, logic, speech, languages, covered by anthropology, linguistics, social sciences etc.

Before we can ask about the mechanisms and the origin and maintenance of body plans, we need to ask what is currently responsible for the development of complex multicellularity, and organismal architecture, form, and cell shape.
We need to understand how an organism develops to adulthood, which permits us with that framework as a starting point to do top-down research to understand how the responsible tool kit and rules for organismal complexity could have emerged in the past.
In fact, it is a development program, which sets how a multicellular organism develops. So we have to define what that development program consists of, in order to know what has to change, for an organism to change its physiology and complexity.

So that change of the development program is what would have to change for an organism to change, and that has given rise to very varied programs of evolutionary disciplines and research programs.
It has become more and more evidently clear, that a varied multitude of different mechanisms is responsible for body constructions, which are not limited to genetics, but mainly, if not even more important, epigenetic factors,

and not only on an intracellular level, but physiology on a multilayered level, which is investigated in systems biology.

The real mechanisms that explain biodiversity and complex organismal architecture is preprogrammed instructional complex INFORMATION encoded in various genetic and epigenetic languages and communication by various signalling codes through various signalling networks.

That brings us to the origin of all life forms by an intelligent designer.
Last edited by Admin on Sun Nov 17, 2019 8:28 am; edited 15 times in total