The seven day Circadian Rhythms: "Nature's Intricate Clockwork"
https://reasonandscience.catsboard.com/t1487-the-seven-day-circadian-rhythms-nature-s-intricate-clockwork
It is already known that the human body maintains its own biological clock. He has a "circadian rhythm" internal 24 hours that drives the increase and the reduction of many molecules. Chronobiology has documented how human beings are highly rhythmic. Most of the many tick tacks are difficult to detect; they operate just below the human consciousness. Innate and hidden in the cell structure, the mysteries of biological time have been revealed by modern computers and scientific advance. I knew about the 24 hours circadian rhytm for some time, but surprisingly there is also a 7-day cycle (Circaseptan Rhythm) . It was detected and related to the record of geomagnetic disturbances (Kp-Index) over a time period of 59-years, (Halberg 1991) Jeremy Campbell says in his book: "The circaceptan pace is one of the big surprises that emerged in modern Chronobiology. Some years ago, few scientists would have expected that biological cycles of seven days would become so widespread and established.
The existence of such precise circaceptan endogenous rhythms (including the need to seven days excretion of 17-ketosteroids [urinary metabolites] in healthy men) suggests that all circaceptanos rhythms are endogenous actually - described as a "built-in" (genetically determined) on the exact period of seven days. 1
What’s the Healthiest Day?: Circaseptan (Weekly) Rhythms in Healthy Considerations 2
Biological clocks govern numerous aspects of human health, including weekly clocks–called circaseptan rhythms–that typically include early-week spikes for many illnesses.
Conclusions
Just as many illnesses have a weekly clock, so do healthy considerations. Discovery of these rhythms opens the door for a new agenda in preventive medicine, including implications for hypothesis development, research strategies to further explore these rhythms, and interventions to exploit daily cycles in healthy considerations.
Moreover, a seven-day cycle was found in the blood pressure fluctuations in the acid content in the blood, in erythrocytes, in a heartbeat, the oral temperature, the temperature of the female breast, chemical and urine volume, rate of two important neurotransmitters - norepinephrine and epinephrine - and the increase and decrease of various body chemicals, such as coping stress hormone, cortisol. 3
http://www.godward.org/archives/Special%20Articles/7-Day%20Cycle.htm
"By the seventh day God had finished the work he had been doing; so on the seventh day he rested from all his work. And God blessed the seventh day and made it holy, because on it he rested from all the work of creating that he had done" (Gen 2:2-3).
His last act in the creation week was to rest and make holy the seventh day as a memorial to his creation. He closed the cycle of creation at seven days and set the clock of time moving forward to this day. In all life resides that circaseptan beat echoing, like a rifle shot in a vast rock canyon, backward in time to the first seven days of dynamic creation.
Each living thing made testifies of brilliant design, of divine craftsmanship, of marvelous function, of intricate interactions with the environment and other life forms, of mystery, of beauty. From roses to redwoods, from salmon to sharks, from elephants to eagles, all life cries to be inspected, admired and praised for its peculiar display of divine handiwork. Even man marvels in awe when he beholds himself:
"For you created my inmost being; you knit me together in my mother's womb. I praise you because I am fearfully and wonderfully made; your works are wonderful, I know that full well" (Ps 139:13-14).
The fingerprints of a divine creator cover his creation. To behold life on earth in its billions of varieties and go forth claiming it to be the result of blind, random, evolutionary accidents, takes a "faith" and a "belief" that defies understanding or logic.
They are of ancient origin, appearing in primitive single-celled organisms, and are thought to be present even in bacteria, the simplest form of life now existing "(p.75).
Wiki confirms:
The circadian rythm is as old as life, existing in Cianobacteria. According to Wiki : The variations of the timing and duration of biological activity in living organisms occur for many essential biological processes. These occur (a) in animals (eating, sleeping, mating, hibernating, migration, cellular regeneration, etc.), (b) in plants (leaf movements, photosynthetic reactions, etc.), and in microbial organisms such as fungi and protozoa. They have even been found in bacteria, especially among the cyanobacteria (aka blue-green algae, see bacterial circadian rhythms). The most important rhythm in chronobiology is the circadian rhythm, a roughly 24-hour cycle shown by physiological processes in all these organisms. How could such sophisticated mechanisms be result of natural , unguided mechanisms ? hard to believe...
The circadian "clock" in humans
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Suprachiasmatic_nucleus
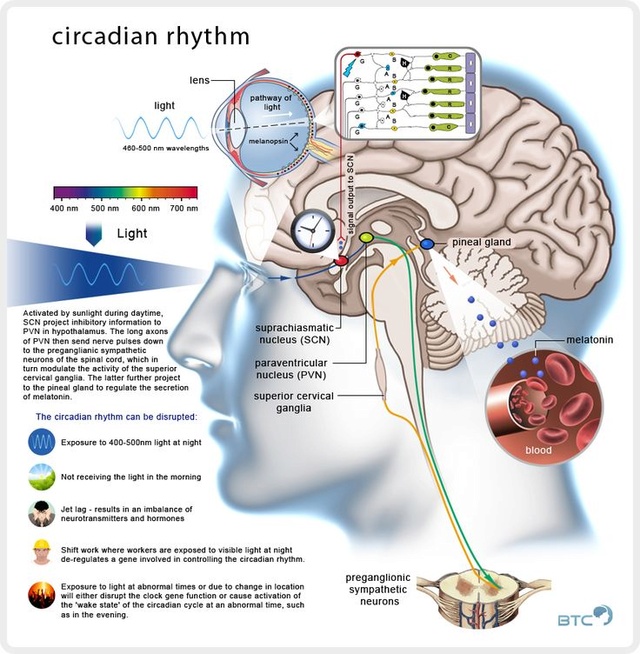
The circadian "clock" in humans is located mainly in the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN), which is a group of cells located in the hypothalamus (a portion of the brain).The suprachiasmatic nucleus or nuclei (SCN) is a tiny region located in the hypothalamus, situated directly above the optic chiasm. It is responsible for controlling circadian rhythms. The neuronal and hormonal activities it generates regulate many different body functions in a 24-hour cycle, using around 20,000 neurons.[1] The SCN interacts with many other regions of the brain. It contains several cell types and several different peptides (including vasopressin and vasoactive intestinal peptide) and neurotransmitters.
I knew about the 24h circadian rhytm for some time, but surprisingly there is also a 7-day cycle (Circaseptan Rhythm)
What’s the Healthiest Day?: Circaseptan (Weekly) Rhythms in Healthy Considerations
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Circadian_rhythm
A circadian rhythm is any biological process that displays an endogenous, entrainable oscillation of about 24 hours. These rhythms are driven by a circadian clock, and rhythms have been widely observed in plants, animals, fungi and cyanobacteria. The term circadian comes from the Latin circa, meaning "around" (or "approximately"), and diem or dies, meaning "day". The formal study of biological temporal rhythms, such as daily, tidal, weekly, seasonal, and annual rhythms, is called chronobiology. Although circadian rhythms are endogenous ("built-in", self-sustained), they are adjusted (entrained) to the local environment by external cues called zeitgebers, commonly the most important of which is daylight.
http://www.evolutionnews.org/2012/09/circadian_rhyth063881.html
"Over the past decade, remarkable progress has been made in elucidating the molecular genetics of these single-cell oscillators," he writes. "More recently, structural biology has begun to contribute a detailed picture of our clock components." The ghost of William Paley studying components of a watch found on a heath rises at the sound of statements like this. (Emphasis added in all quotations.)
Crane was commenting on work by Huang et al., in the same issue of Science. (see our June 5 article). They identified two proteins that are part of the "autoregulatory transcriptional feedback mechanism that takes approximately 24 hours to complete." The proteins form a complex that "controls the expression of numerous genes, including those that code for the oscillator proteins of the clock itself." These proteins, CLOCK and BMAL1, are "made up of two domains that are found throughout biology, serving a range of functions." Moreover, they contain numerous interfaces to other proteins.
http://www.sciencemag.org/content/337/6091/165.summary
Much of human physiology and behavior is influenced by circadian rhythms. Whether you burned the midnight oil, rose at the crack of dawn, or enjoyed your rest last night, tiny clocks in your cells have been trying to keep you on schedule. Over the past decade, remarkable progress has been made in elucidating the molecular genetics of these single-cell oscillators. More recently, structural biology has begun to contribute a detailed picture of our clock components.
The circadian clock is like an orchestra with many conductors
http://phys.org/news/2014-03-circadian-clock-orchestra-conductors.html
http://www.suspicious0bserverscollective.org/the-blog/rhythms-of-life-circadian-circaseptan-schumann-resonances-human-health
In addition to the Circadian Rhythm, which is a bi-product of the 24-hour rotational cycle (day/night) of the Earth, there is the Circaseptan Rhythm, a 7-day cycle that correlates to the Geomagnetic Activity of Earth. As detailed in Dr. Cherry's model, changes in the Schumann Resonance via S-GMA induces changes in the cellular calcium ion signals, brain wave patterns and reactions times which produces altered melatonin/serotonin production. When this neurohormone chemistry is altered by the circadian cycle, a wide range of organs and bodily processes are influenced affecting human health.
1. Levi F, Halberg F. Circaseptan (about-7-day) bioperiodicity - spontaneous and reactive -and the search for pacemakers. Ric Clin Lab. 1982 Apr-Jun;12(2):323-70. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7111982
2. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0749379714000993
3. Haus E .Chronobiology in the endocrine system. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2007; 59(9-10):985-1014. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17804113
read more :
http://reasonandscience.heavenforum.org/t1487-the-seven-day-circadian-rhythms-nature-s-intricate-clockwork#2164
https://reasonandscience.catsboard.com/t1487-the-seven-day-circadian-rhythms-nature-s-intricate-clockwork

It is already known that the human body maintains its own biological clock. He has a "circadian rhythm" internal 24 hours that drives the increase and the reduction of many molecules. Chronobiology has documented how human beings are highly rhythmic. Most of the many tick tacks are difficult to detect; they operate just below the human consciousness. Innate and hidden in the cell structure, the mysteries of biological time have been revealed by modern computers and scientific advance. I knew about the 24 hours circadian rhytm for some time, but surprisingly there is also a 7-day cycle (Circaseptan Rhythm) . It was detected and related to the record of geomagnetic disturbances (Kp-Index) over a time period of 59-years, (Halberg 1991) Jeremy Campbell says in his book: "The circaceptan pace is one of the big surprises that emerged in modern Chronobiology. Some years ago, few scientists would have expected that biological cycles of seven days would become so widespread and established.
The existence of such precise circaceptan endogenous rhythms (including the need to seven days excretion of 17-ketosteroids [urinary metabolites] in healthy men) suggests that all circaceptanos rhythms are endogenous actually - described as a "built-in" (genetically determined) on the exact period of seven days. 1
What’s the Healthiest Day?: Circaseptan (Weekly) Rhythms in Healthy Considerations 2
Biological clocks govern numerous aspects of human health, including weekly clocks–called circaseptan rhythms–that typically include early-week spikes for many illnesses.
Conclusions
Just as many illnesses have a weekly clock, so do healthy considerations. Discovery of these rhythms opens the door for a new agenda in preventive medicine, including implications for hypothesis development, research strategies to further explore these rhythms, and interventions to exploit daily cycles in healthy considerations.
Moreover, a seven-day cycle was found in the blood pressure fluctuations in the acid content in the blood, in erythrocytes, in a heartbeat, the oral temperature, the temperature of the female breast, chemical and urine volume, rate of two important neurotransmitters - norepinephrine and epinephrine - and the increase and decrease of various body chemicals, such as coping stress hormone, cortisol. 3
http://www.godward.org/archives/Special%20Articles/7-Day%20Cycle.htm
"By the seventh day God had finished the work he had been doing; so on the seventh day he rested from all his work. And God blessed the seventh day and made it holy, because on it he rested from all the work of creating that he had done" (Gen 2:2-3).
His last act in the creation week was to rest and make holy the seventh day as a memorial to his creation. He closed the cycle of creation at seven days and set the clock of time moving forward to this day. In all life resides that circaseptan beat echoing, like a rifle shot in a vast rock canyon, backward in time to the first seven days of dynamic creation.
Each living thing made testifies of brilliant design, of divine craftsmanship, of marvelous function, of intricate interactions with the environment and other life forms, of mystery, of beauty. From roses to redwoods, from salmon to sharks, from elephants to eagles, all life cries to be inspected, admired and praised for its peculiar display of divine handiwork. Even man marvels in awe when he beholds himself:
"For you created my inmost being; you knit me together in my mother's womb. I praise you because I am fearfully and wonderfully made; your works are wonderful, I know that full well" (Ps 139:13-14).
The fingerprints of a divine creator cover his creation. To behold life on earth in its billions of varieties and go forth claiming it to be the result of blind, random, evolutionary accidents, takes a "faith" and a "belief" that defies understanding or logic.
They are of ancient origin, appearing in primitive single-celled organisms, and are thought to be present even in bacteria, the simplest form of life now existing "(p.75).
Wiki confirms:
The circadian rythm is as old as life, existing in Cianobacteria. According to Wiki : The variations of the timing and duration of biological activity in living organisms occur for many essential biological processes. These occur (a) in animals (eating, sleeping, mating, hibernating, migration, cellular regeneration, etc.), (b) in plants (leaf movements, photosynthetic reactions, etc.), and in microbial organisms such as fungi and protozoa. They have even been found in bacteria, especially among the cyanobacteria (aka blue-green algae, see bacterial circadian rhythms). The most important rhythm in chronobiology is the circadian rhythm, a roughly 24-hour cycle shown by physiological processes in all these organisms. How could such sophisticated mechanisms be result of natural , unguided mechanisms ? hard to believe...
The circadian "clock" in humans
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Suprachiasmatic_nucleus
The circadian "clock" in humans is located mainly in the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN), which is a group of cells located in the hypothalamus (a portion of the brain).The suprachiasmatic nucleus or nuclei (SCN) is a tiny region located in the hypothalamus, situated directly above the optic chiasm. It is responsible for controlling circadian rhythms. The neuronal and hormonal activities it generates regulate many different body functions in a 24-hour cycle, using around 20,000 neurons.[1] The SCN interacts with many other regions of the brain. It contains several cell types and several different peptides (including vasopressin and vasoactive intestinal peptide) and neurotransmitters.
I knew about the 24h circadian rhytm for some time, but surprisingly there is also a 7-day cycle (Circaseptan Rhythm)
What’s the Healthiest Day?: Circaseptan (Weekly) Rhythms in Healthy Considerations
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Circadian_rhythm
A circadian rhythm is any biological process that displays an endogenous, entrainable oscillation of about 24 hours. These rhythms are driven by a circadian clock, and rhythms have been widely observed in plants, animals, fungi and cyanobacteria. The term circadian comes from the Latin circa, meaning "around" (or "approximately"), and diem or dies, meaning "day". The formal study of biological temporal rhythms, such as daily, tidal, weekly, seasonal, and annual rhythms, is called chronobiology. Although circadian rhythms are endogenous ("built-in", self-sustained), they are adjusted (entrained) to the local environment by external cues called zeitgebers, commonly the most important of which is daylight.
http://www.evolutionnews.org/2012/09/circadian_rhyth063881.html
"Over the past decade, remarkable progress has been made in elucidating the molecular genetics of these single-cell oscillators," he writes. "More recently, structural biology has begun to contribute a detailed picture of our clock components." The ghost of William Paley studying components of a watch found on a heath rises at the sound of statements like this. (Emphasis added in all quotations.)
Crane was commenting on work by Huang et al., in the same issue of Science. (see our June 5 article). They identified two proteins that are part of the "autoregulatory transcriptional feedback mechanism that takes approximately 24 hours to complete." The proteins form a complex that "controls the expression of numerous genes, including those that code for the oscillator proteins of the clock itself." These proteins, CLOCK and BMAL1, are "made up of two domains that are found throughout biology, serving a range of functions." Moreover, they contain numerous interfaces to other proteins.
http://www.sciencemag.org/content/337/6091/165.summary
Much of human physiology and behavior is influenced by circadian rhythms. Whether you burned the midnight oil, rose at the crack of dawn, or enjoyed your rest last night, tiny clocks in your cells have been trying to keep you on schedule. Over the past decade, remarkable progress has been made in elucidating the molecular genetics of these single-cell oscillators. More recently, structural biology has begun to contribute a detailed picture of our clock components.
The circadian clock is like an orchestra with many conductors
http://phys.org/news/2014-03-circadian-clock-orchestra-conductors.html
http://www.suspicious0bserverscollective.org/the-blog/rhythms-of-life-circadian-circaseptan-schumann-resonances-human-health
In addition to the Circadian Rhythm, which is a bi-product of the 24-hour rotational cycle (day/night) of the Earth, there is the Circaseptan Rhythm, a 7-day cycle that correlates to the Geomagnetic Activity of Earth. As detailed in Dr. Cherry's model, changes in the Schumann Resonance via S-GMA induces changes in the cellular calcium ion signals, brain wave patterns and reactions times which produces altered melatonin/serotonin production. When this neurohormone chemistry is altered by the circadian cycle, a wide range of organs and bodily processes are influenced affecting human health.
1. Levi F, Halberg F. Circaseptan (about-7-day) bioperiodicity - spontaneous and reactive -and the search for pacemakers. Ric Clin Lab. 1982 Apr-Jun;12(2):323-70. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7111982
2. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0749379714000993
3. Haus E .Chronobiology in the endocrine system. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2007; 59(9-10):985-1014. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17804113
read more :
http://reasonandscience.heavenforum.org/t1487-the-seven-day-circadian-rhythms-nature-s-intricate-clockwork#2164

